Representation of Numbers on the Abacus
We will learn representation of numbers on the abacus.
Numbers on Abacus:
|
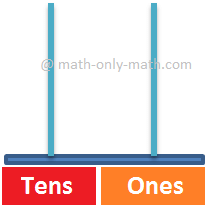
This abacus is having two spikes. Spike on the left is Tens spike and spike on the right is Ones spike. |
The number of beads placed in Ones spike reads Ones number and the number of beads in Tens spike reads Tens number.
|
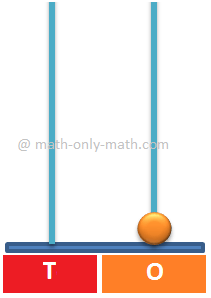
Showing 1 at Ones place and 0 at Tens place. So, the number is 0 Tens and 1 Ones - 1 Therefore, it is showing the number 1. |
|
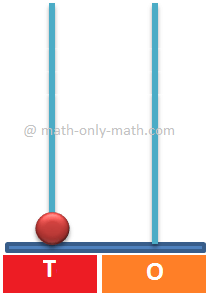
Showing 0 at Ones place and 1 at Terns place. So, the number is One Tens and 0 Ones - 10 Therefore, it is showing the number 10. |
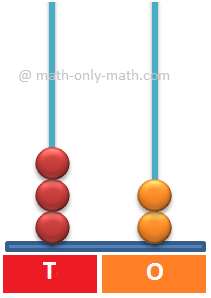
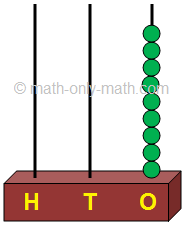
We can show 100 on an abacus with three vertical rods. The rods represent place value of hundreds, tens and ones. We add beads on the rods to show different number. Each rod can hold up to 9 beads.
|
This shows 9 ones |
If we add 1 more to 9 it is 10 ones. Regroup 10 ones as 1 ten. |
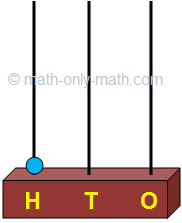
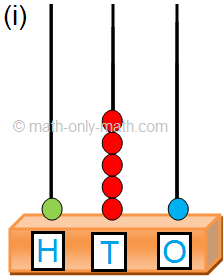
This shows 9 tens and 9 ones. The number is 99. |
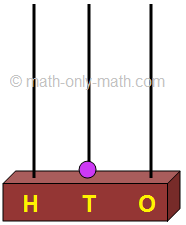
If we add 1 more to 99 it is 10 tens. Regroup 10 tens as 1 hundred. |
1 bead in the hundreds place represents 1 hundred.
To read a 3-digit number first read the hundreds place and then the last two digits place.
Let us take this example:
|
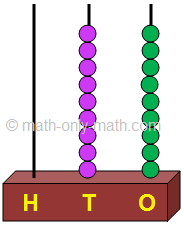
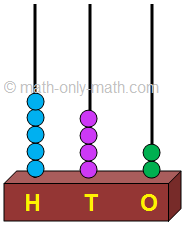
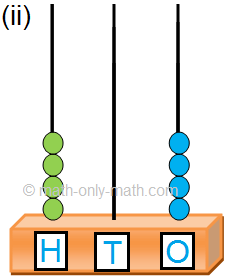
5 beads in the hundreds place means 5 hundreds. 4 beads in the tens place means 4 tens. 2 beads in the ones place means 2 ones.
The number can be written as 542 = 5 hundreds 4 tens and 2 ones Five hundred forty-two |
Questions and Answers on Representation of Numbers on the Abacus:
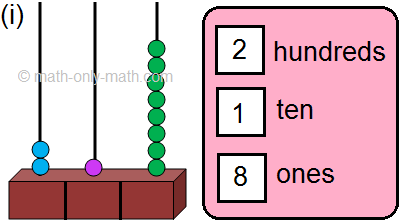
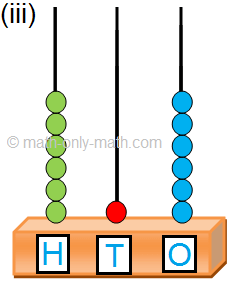
1. Read the following numbers on the abacus and write the number names in the given space.
Answer:
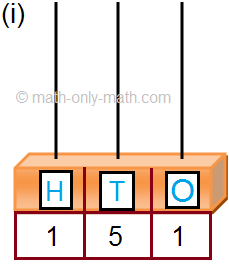
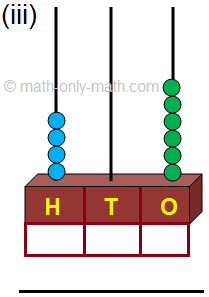
1. (i) One hundred twenty-seven.
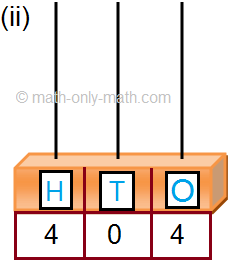
(ii) Two hundred seven.
(iii) Three hundred twenty-nine.
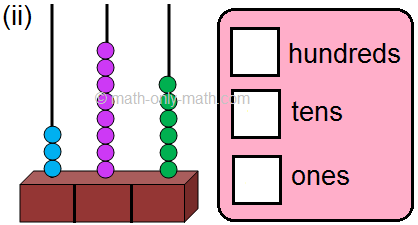
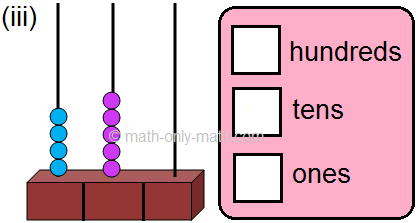
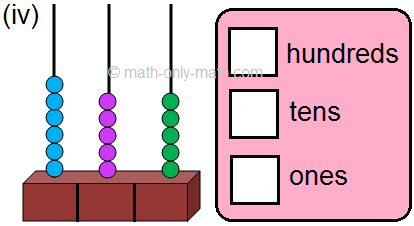
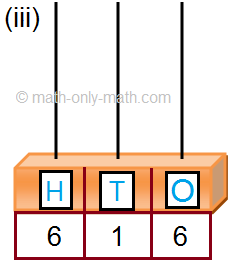
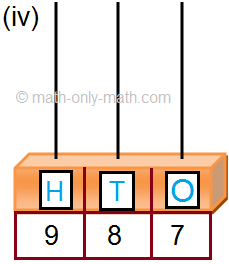
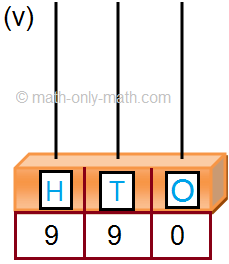
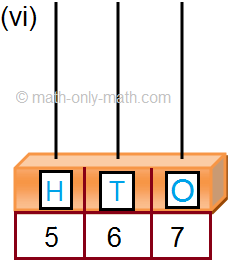
2. Read the given number on the abacus and fill in the blanks. One has been done for you.
Answer:
2. (ii) 3 hundreds; 8 tens; 6 ones
(iii) 4 hundreds; 5 tens; 0 ones
(iv) 6 hundreds; 5 tens; 5 ones
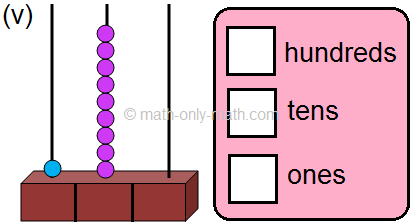
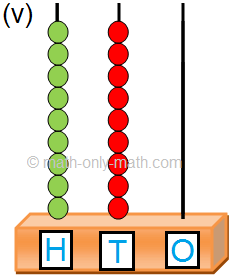
(v) 1 hundreds; 9 tens; 0 ones
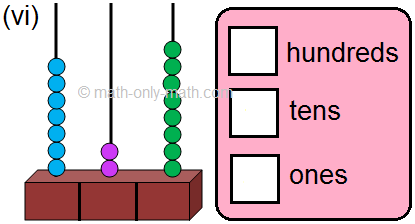
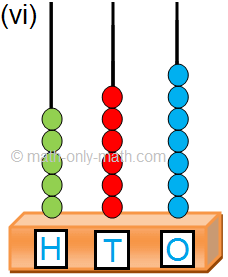
(vi) 7 hundreds; 2 tens; 8 ones
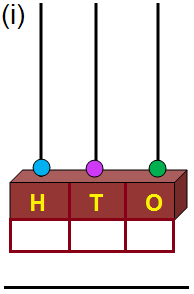
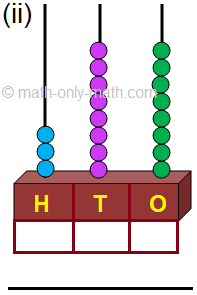
3. Draw beads to show the following numbers on the abacus.
Answer:
3.
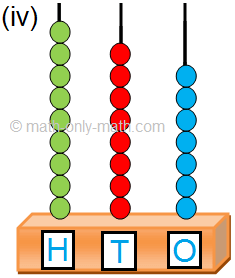
4. Read the numbers shown on the abacus. Write the number and the number name in the given space.
Answer:
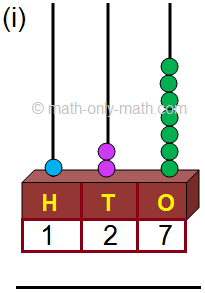
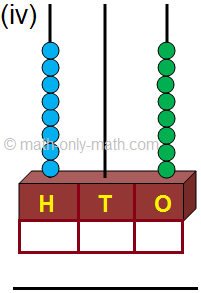
4. (i) 111; One hundred one
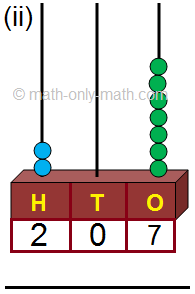
(ii) 388; Three hundred eighty-eight.
(iii) 406; Four hundred six
(iv) 808; Eight hundred eight
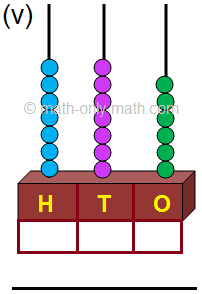
(v) 776; Seven hundred seventy-six
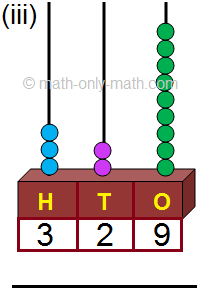
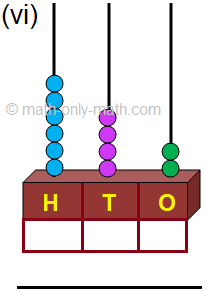
(vi) 642; Six hundred forty-two
From Representation of Numbers on the Abacus to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Counting Numbers from 1 to 50 | Match the Number | Missing Numbers
Apr 04, 25 03:46 PM
In counting numbers from 1 to 50, recognize the numbers, count and then join the numbers in the correct number order. Here we mainly need eye-hand coordination to draw the picture and maintain the num -
Counting Eleven to Twenty with Numbers and Words |Numbers from 11 - 20
Apr 04, 25 03:21 PM
Counting eleven to twenty with numbers and words are explained below. One ten and one more is eleven. Eleven comes after ten. One ten and two more is twelve. Twelve comes after eleven. -
5th Grade BODMAS Rule Worksheet | PEMDAS | Order of operations|Answers
Apr 03, 25 03:11 PM
In 5th Grade BODMAS Rule Worksheet you will get different types of problems on mathematical expressions involving different operations, mathematical expression with 'brackets' and 'of' and simplifying… -
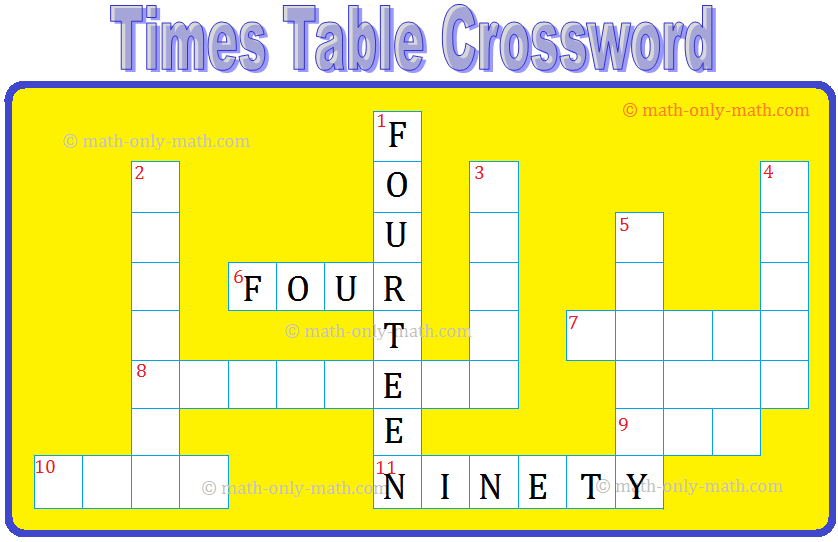
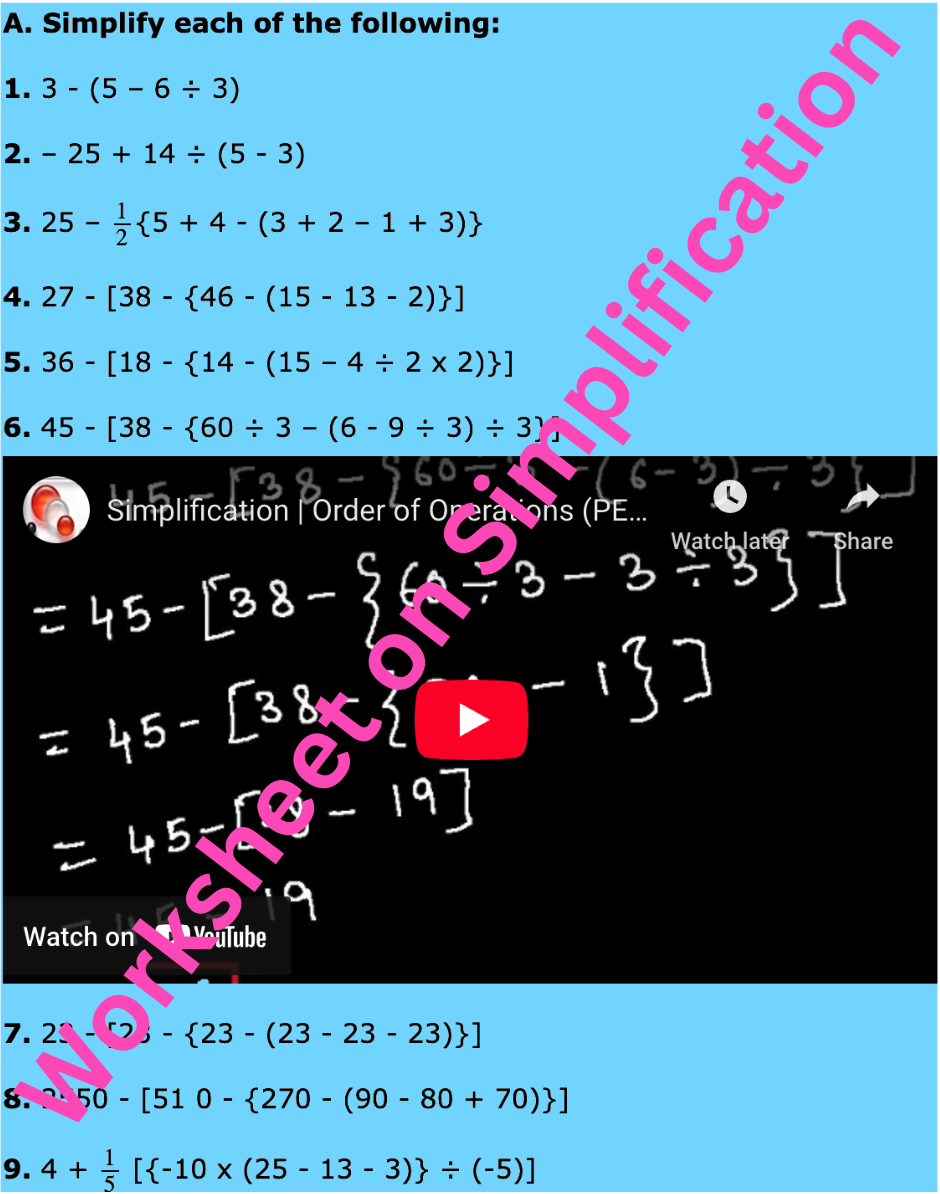
Worksheet on Simplification | Simplify Expressions | BODMAS Questions
Apr 03, 25 02:58 PM
In worksheet on simplification, the questions are based in order to simplify expressions involving more than one bracket by using the steps of removal of brackets. This exercise sheet -
Divisible by 2 Video |Test of Divisibility by 2 Trick| Rules| Examples
Apr 03, 25 10:25 AM
A number is divisible by 2 if the digit at unit place is either 0 or multiple of 2. So a number is divisible by 2 if digit at its units place is 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8.














New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.