Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Divide by Repeated Subtraction
How to divide by repeated subtraction?
We will learn how to find the quotient and remainder by the method of repeated subtraction a division problem may be solved.
DIVISION AS REPEATED SUBTRACTION
As multiplication is repeated addition, division is repeated subtraction.
Let us see how.
We know that division is equal distribution of objects.
When we divide, we find out how many times we can subtract the given number from the group of objects.
Equal sharing or grouping can also be done by repeated subtraction.
Example:
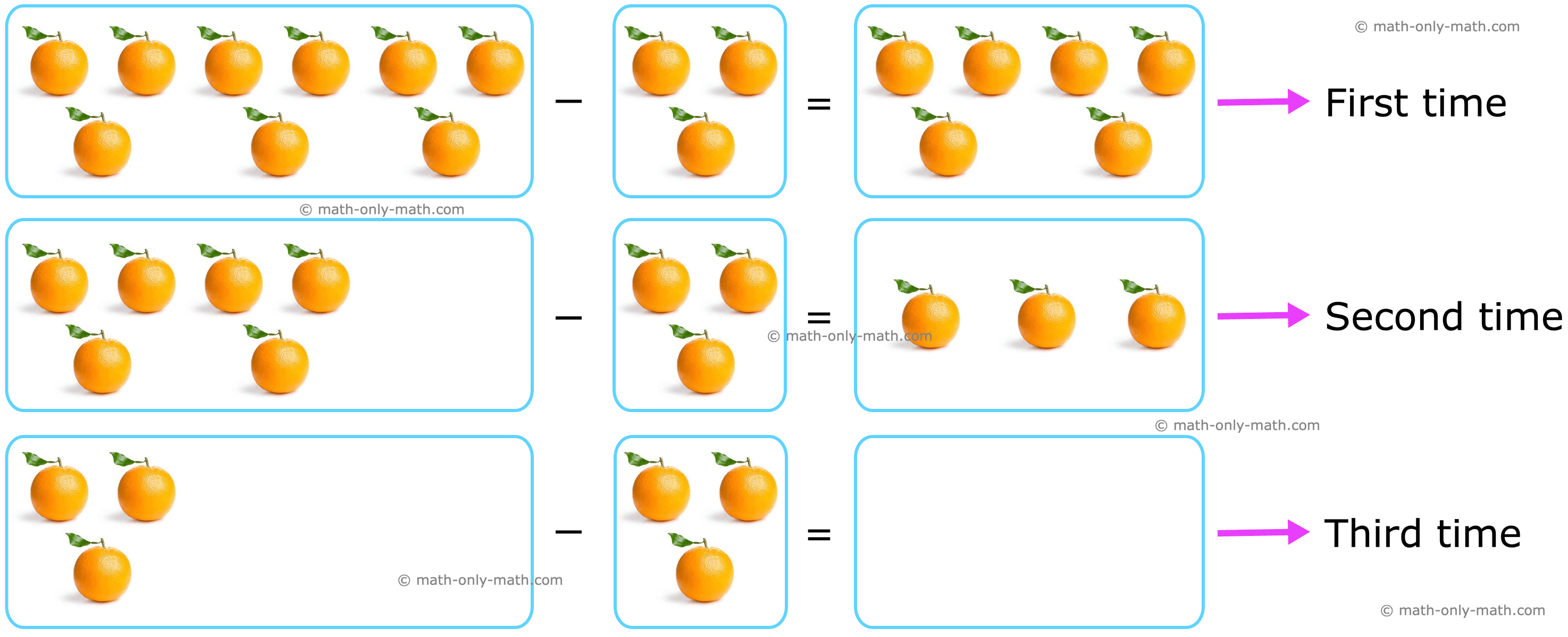
Divide 9 apples among 3 children by repeated subtraction.
To divide 9 apples among 3 children, we subtract 3 from 9 repeatedly until we get 0.
Since 9 apples have been subtracted three times to get 0, so 9 ÷ 3 = 3
Dividing Using Repeated Subtraction Short Video
Let us understand this with the help of more following examples.
Divide by Repeated Subtraction
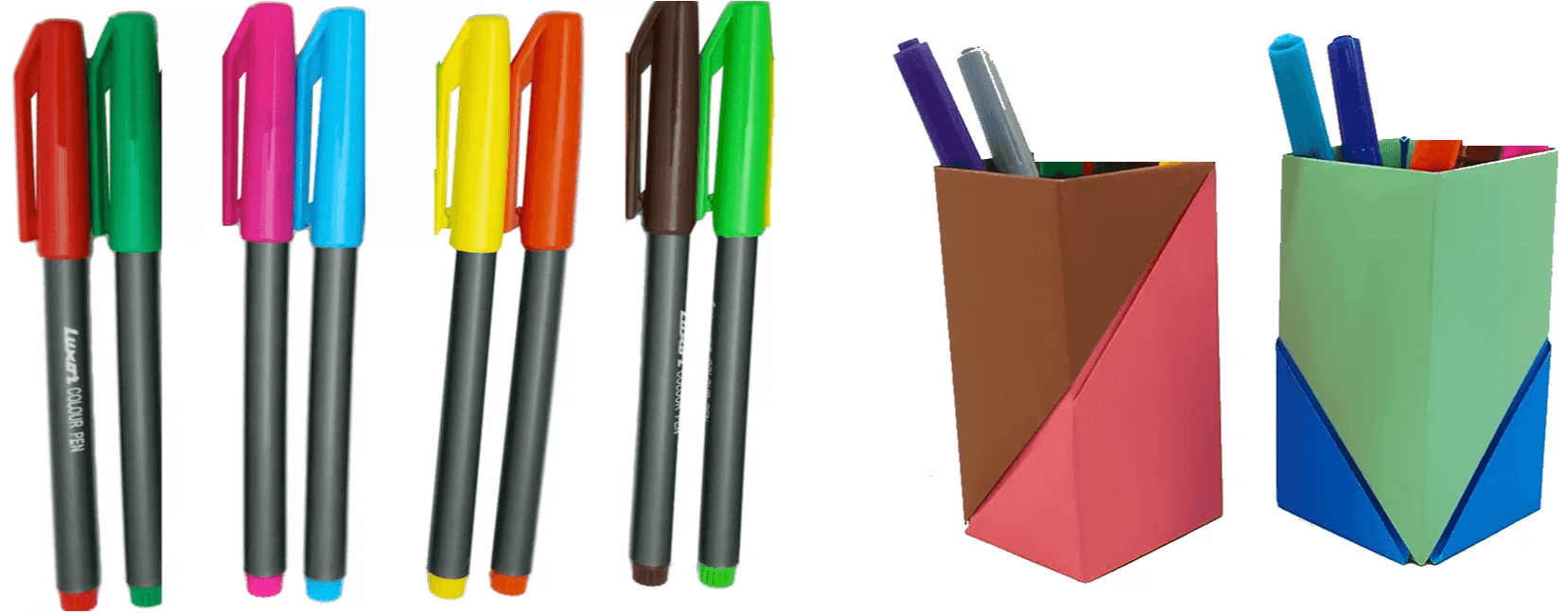
1. 12 pens have to be equally kept in 2 penstands.
So, how many times can 2 be taken away from 12?
Let us subtract 2 again and again from 12 till we reach 0.
How many times 2 has been subtracted from 12 to reach 0? Clearly, 6
Therefore, 12 ÷ 2=6
Solved examples on divide by repeated subtraction:
1. Solve 16 ÷ 8
Solution:
8 is subtracted repeatedly from 16 as shown:
When 8 is subtracted from 16, 2 times, then we get the remainder zero.
Hence, 16 ÷ 8 = 2, 2 is the quotient.
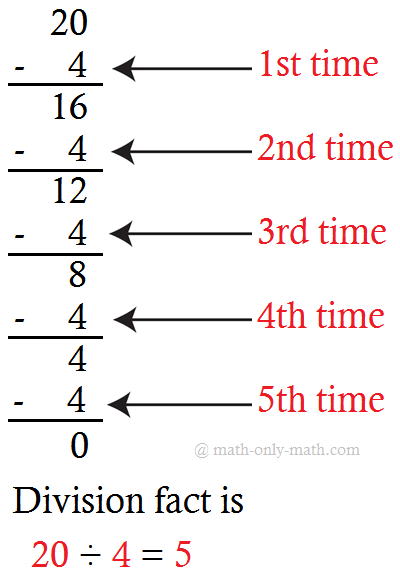
2. Divide 20 ÷ 5
5 is subtracted repeatedly from 20 as shown:
When 5 is
subtracted from 20, four times, then we get the remainder zero.
Hence, 20 ÷ 5 = 4, 4 is the quotient.
3. Solve 12 by 3
Solution:
3 is subtracted repeatedly from 12 as shown:
When 3 is
subtracted from 12, four times, then we get the remainder zero.
Hence, 12 ÷ 3 = 4, 4 is the quotient.
4. Divide 28 ÷ 7
7 is subtracted repeatedly from 28 as shown:
When 7 is
subtracted from 28, four times, then we get the remainder zero.
Hence, 28 ÷ 7 = 4, 4 is the quotient.
5. Divide 32 ÷ 4
4 is subtracted repeatedly from 32 as shown:
When 4 is
subtracted from 32, eight times, then we get the remainder zero.
Hence, 32 ÷ 4 = 8, 8 is the quotient.
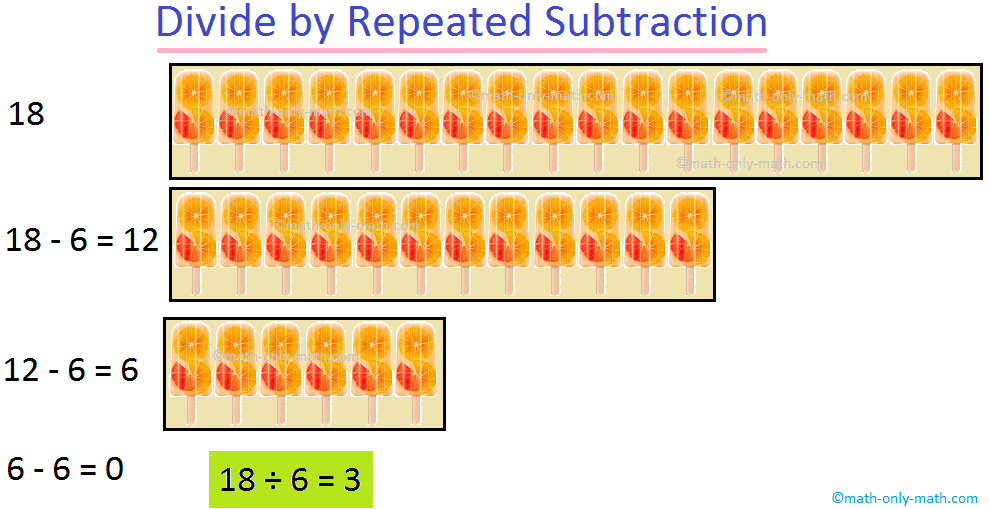
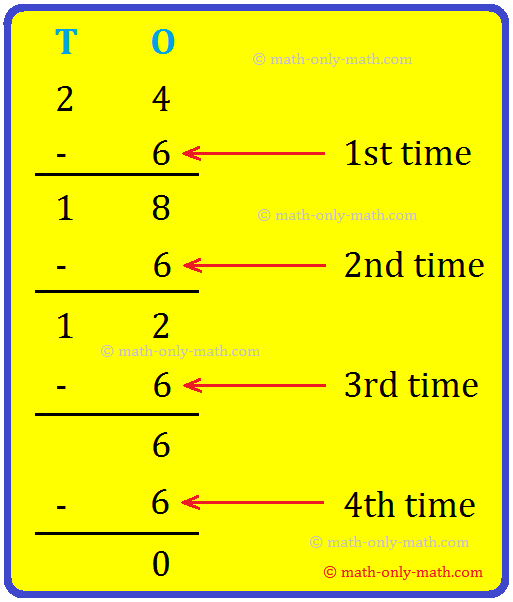
6. Solve 18 by 6.
6 is subtracted repeatedly from 18 as shown:
When 6 is subtracted from 18, three times, then we get the remainder zero.
Hence, 18 ÷ 6 = 3, 3 is the quotient.
7. Divide 12 flowers in 3 vases.
We put 1 flower in each of the 3 vases and subtract 3 from 12 each time.
12 – 3 = 9
9 – 3 = 6
6 – 3 = 3
3 – 3 = 0
There are no more flowers left. We subtracted 4 times 3 from 12.
We subtract 3 flowers 4 times from 12 to get 0.
7. Divide 18 ice creams among 6 children by repeated subtraction.
8. Find 12 ÷ 4 by repeated subtraction.
Example:
12 - 4 = 8 → 8 - 4 = 4 → 4 - 4 = 0
4 can be subtracted 3 times from 12. So, 12 ÷ 4 = 3
Division as Repeated Subtraction
9. This is a basket. There are 15 apples in the basket.
Step I: Take 3 apples from the basket.
12 apples are left in the basket.
15 - 3 = 12
Step II: Take 3 more apples from basket.
Now, 9 apples are left in the basket.
12 - 3 = 9
Step III: Take 3 more apples from the basket.
Now, 6 apples are left in the basket.
9 - 3 = 6
Step IV: Take 3 more apples from the basket.
Now, 3 apples are left in the basket.
6 - 3 = 3
Step V: Now, take 3 more apples from the basket.
We find that no apple is left in the basket.
3 - 3 = 0
We have repeatedly subtracted 3 from 15 and we have done it 5 times.
So, 15 ÷ 3 = 5
Thus, division is called repeated subtraction of the same number.
10. Nitheeya has 24 tofees. She has to distribute these among her 6 friends. How many toffees will she give to each friend?
She starts giving 1 toffee to each friend and repeats this act till all the toffees are over. This goes on 4 times.
Each friend gets 4 sweets.
So, 24 ÷ 6 = 4
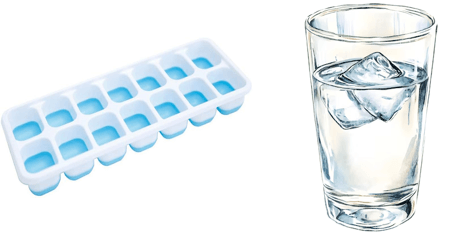
11. There are 14 ice cubes in a tray. 2 ice cubes have to be put in each glass of juice. How many glasses are needed?
Solution:
|
Put 2 ice cubes in the first glass. |
14 - 2 = 12 | |
|
Put 2 ice cubes in the second glass. |
12 - 2 = 10 | |
|
Put 2 ice cubes in the third glass. |
10 - 2 = 8 | |
|
Put 2 ice cubes in the fourth glass. |
8 - 2 = 6 | |
|
Put 2 ice cubes in the fifth glass. |
6 - 2 = 4 | |
|
Put 2 ice cubes in the sixth glass. |
4 - 2 = 2 | |
|
Put 2 ice cubes in the seventh glass. |
2 - 2 = 0 |
No more ice cubes are left. Thus, we distributed 14 ice cubes in this way:
14 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2
Or, we can say that we subtracted 2 seven times from 14.
Therefore, 14 ÷ 2 = 7
The above examples will help us to solve various division problems on 2-digit number by a single digit number using the method of repeated subtraction.
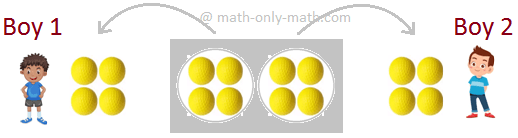
Division by Equal Distribution:
When 8 balls are equally distributed in 2 boys, we write 8 ÷ 2 = 4
Worksheet on Divide by Repeated Subtraction:
Questions and Answers on Divide by Repeated Subtraction:
1. Divide using repeated subtraction. One has been done for you.
(i) Divide 16 by 4.
|
T O 1 6 - 4 1 2 |
T O 1 2 - 4 8 |
T O 8 - 4 4 |
T O 4 - 4 0 |
16 ÷ 4 = 4 |
(ii) Divide 6 by 2.
|
T O 6 - 2
|
T O
|
T O
|
T O
|
6 ÷ 2 = __ |
(iii) Divide 12 by 3.
|
T O 1 2 - 3
|
T O
|
T O
|
T O
|
12 ÷ 3 = __ |
(iv) Divide 20 by 5.
|
T O 2 0 - 5
|
T O
|
T O
|
T O
|
20 ÷ 5 = __ |
(v) Divide 14 by 7.
|
T O 1 4 - 7
|
T O
|
T O
|
T O
|
14 ÷ 7 = __ |
Answer:
1. (ii)
|
T O 6 - 2 4 |
T O 4 - 2 2 |
T O 2 - 2 0 |
|
6 ÷ 2 = 3 |
(ii)
|
T O 1 2 - 3 9 |
T O 9 - 3 6 |
T O 6 - 3 3 |
T O 3 - 3 0 |
12 ÷ 3 = 4 |
(iii)
|
T O 2 0 - 5 1 5 |
T O 1 5 - 5 1 0 |
T O 1 0 - 5 5 |
T O 5 - 5 0 |
20 ÷ 5 = 4 |
(iv)
|
T O 1 4 - 7 7 |
T O 7 - 7 0 |
|
|
14 ÷ 7 = 2 |
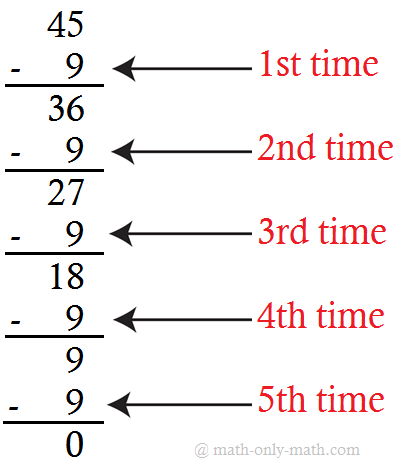
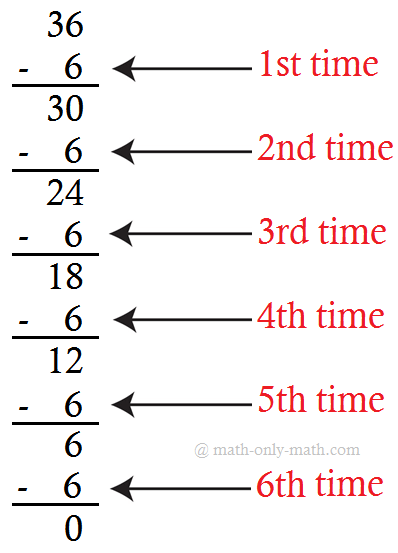
2. Write the following subtractions as division facts. One has been done for you.
(i)
Answer:
1. (ii) 45 ÷ 9 = 5
(iii) 36 ÷ 6 = 6
3. Write the following division facts as repeated subtractions. One has been done for you.
(i) 20 ÷ 5 = 4
Repeated subtraction for the given fact is:
|
(ii) |
35 ÷ 7 = 5 Repeated subtraction for the given fact is: |
(iii) |
48 ÷ 6 = 8 Repeated subtraction for the given fact is: |
4. Divide the following using repeated subtraction. One has been done for you:
|
(i) |
6 ÷ 2 6 - 2 = 4 4 - 2 = 2 2 - 2 = 0 Therefore, 6 ÷ 2 = 3 |
(ii) |
24 ÷ 8 __ ÷ __ = __ __ ÷ __ = __ __ ÷ __ = __ Therefore, __ ÷ __ = __ |
|
(iii) |
18 ÷ 6 __ ÷ __ = __ __ ÷ __ = __ __ ÷ __ = __ Therefore, __ ÷ __ = __ |
(iv) |
16 ÷ 4 __ ÷ __ = __ __ ÷ __ = __ __ ÷ __ = __ __ ÷ __ = __ Therefore, __ ÷ __ = __ |
Answer:
4. (ii) 24 ÷ 8
24 - 8 = 16
16 - 8 = 8
8 - 8 = 0
Therefore,
24 ÷ 8 = 3
(ii) 18 ÷ 6
18 - 6 = 12
12 - 6 = 6
6 - 6 = 0
Therefore,
18 ÷ 6 = 3
(ii) 16 ÷ 4
16 - 4 = 12
12 - 4 = 8
8 - 4 = 4
4 - 4 = 0
Therefore,
16 ÷ 4 = 4
5. Write the division fact for the following:
(i) 35 - 7 - 7 - 7 - 7 - 7 → = ___ ÷ ___ = ___
(ii) 20 - 5 - 5 - 5 - 5 → = ___ ÷ ___ = ___
Answer:
5. (i) 35 ÷ 7 = 5
(ii) 20 ÷ 5 = 4
6. Find out how many children will get the apples:
(i) Each child gets 12 apples.
|
24 |
|
in equal groups of 12 = __________ groups |
24 ÷ 12 = _____
Therefore, _____ children will get 12 apples each.
(ii) Each child gets 4 apples.
|
24 |
|
in equal groups of 4 = __________ groups |
24 ÷ 4 = _____
Therefore, _____ children will get 4 apples each.
(iii) Each child gets 3 apples.
|
24 |
|
in equal groups of 3 = __________ groups |
24 ÷ 3 = _____
Therefore, _____ children will get 3 apples each.
When we make equal groups, we know how many are in each group.
Answer:
6. (i) 2; 2; 2
(ii) 6; 6; 6
(iii) 8; 8; 8
7. Now, divide the following using the repeated subtraction method:
|
(i) |
25 ÷ 5 |
(ii) |
16 ÷ 4 |
|
(iii) |
12 ÷ 4 |
(iv) |
36 ÷ 6 |
|
(v) |
42 ÷ 7 |
(vi) |
48 ÷ 8 |
From Divide by Repeated Subtraction to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.





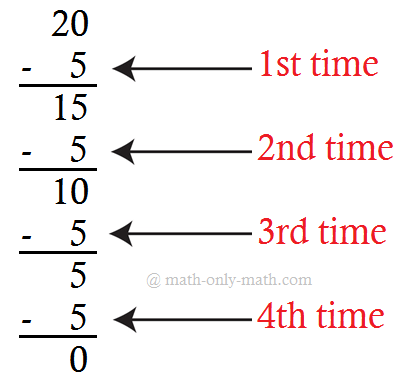


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.