Standard Equation of an Ellipse
We will learn how to find the standard equation of an ellipse.
Let S be the focus, ZK the straight line (directrix) of the ellipse and e (0 < e < 1) be its eccentricity. From S draw SK perpendicular to the directrix KZ. Suppose the line segment SK is divided internally at A and externally at A' (on KS produced) respectively in the ratio e : 1.
Therefore, \(\frac{SA}{AK}\) = e : 1
\(\frac{SA}{AK}\) = \(\frac{e}{1}\)
⇒ SA = e ∙ AK ...................... (i) and
\(\frac{SA'}{A'K}\) = e : 1
\(\frac{SA'}{A'K}\) = \(\frac{e}{1}\)
⇒ SA' = e ∙ A'K ...................... (ii)
We can clearly see that the points A and A'' lies on
the ellipse since, their distance from the focus (S) bear constant ratio e
(< 1) to their respective distance from the directrix.
Let C be the mid-point of the line-segment AA'; draw CY perpendicular to AA'.
Now, let us choose C as the origin CA and CY are chosen as x and y-axes respectively.
Therefore, AA' = 2a
⇒ A'C = CA = a.
Now, adding (i) and (ii) we get,
SA + SA' = e (AK + A'K)
⇒ AA' = e (CK - CA + CK + CA')
⇒ 2a = e (2CK - CA + CA')
⇒ 2a = 2e ∙ CK, (Since, CA = CA')
⇒ CK = \(\frac{a}{e}\) ...................... (iii)
Similarly, subtracting (i) from (ii) we get,
SA' - SA = e (KA' - AK)
⇒ (CA' + CS) - (CA - CS) = e . (AA')
⇒ 2CS = e ∙ 2a, [Since, CA' = CA]
⇒ CS = ae ...................... (iv)
Let P (x, y) be any point on the required ellipse. From P draw PM perpendicular to KZ and PN perpendicular to CX and join SP.
Then, CN = x, PN = y and
PM = NK = CK - CN = \(\frac{a}{e}\) – x, [Since, CK = \(\frac{a}{e}\)] and
SN = CS - CN = ae - x, [Since, CS = ae]
Since the point P lies on the required ellipse, Therefore, by the definition we get,
\(\frac{SP}{PM}\) = e
⇒ SP = e ∙ PM
⇒ SP\(^{2}\) = e\(^{2}\) . PM\(^{2}\)
or (ae - x)\(^{2}\) + (y - 0)\(^{2}\) = e\(^{2}\)[\(\frac{a}{e}\) - x]\(^{2}\)
⇒ x\(^{2}\)(1 – e\(^{2}\)) + y\(^{2}\) = a\(^{2}\)(1 – e\(^{2}\))
⇒ \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}\) + \(\frac{y^{2}}{a^{2}(1 - e^{2})}\) = 1
⇒ \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}\) + \(\frac{y^{2}}{a^{2}(1 - e^{2})}\) = 1
Since
0 < e < 1, hence a\(^{2}\)(1 - e\(^{2}\)) is always positive;
therefore, if a\(^{2}\)(1 - e\(^{2}\))
= b\(^{2}\), the above equation becomes, \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}\) + \(\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}\) = 1.
The relation \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}\) + \(\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}\) = 1 is satisfied by the co-ordinates of all points P (x, y) on the required ellipse and hence, represents the required equation of the ellipse.
The equation of an ellipse in the form \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}\) + \(\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}\) = 1 is called the standard equation of the ellipse.
Notes:
(i) b\(^{2}\) < a\(^{2}\), since e\(^{2}\) < 1 and b\(^{2}\) = a\(^{2}\)(1 - e\(^{2}\))
(ii) b\(^{2}\) = a\(^{2}\)(1 – e\(^{2}\))
⇒ \(\frac{b^{2}}{a^{2}}\) = 1 – e\(^{2}\), [Dividing both sides by a\(^{2}\)]
⇒ e\(^{2}\) = 1 - \(\frac{b^{2}}{a^{2}}\)
⇒ e = \(\sqrt{ 1 - \frac{b^{2}}{a^{2}}}\), [taking square root on both sides]
Form the above relation e = \(\sqrt{ 1 - \frac{b^{2}}{a^{2}}}\), we can find the value of e when a and b are given.
● The Ellipse
- Definition of Ellipse
- Standard Equation of an Ellipse
- Two Foci and Two Directrices of the Ellipse
- Vertex of the Ellipse
- Centre of the Ellipse
- Major and Minor Axes of the Ellipse
- Latus Rectum of the Ellipse
- Position of a Point with respect to the Ellipse
- Ellipse Formulae
- Focal Distance of a Point on the Ellipse
- Problems on Ellipse
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Standard Equation of an Ellipse to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
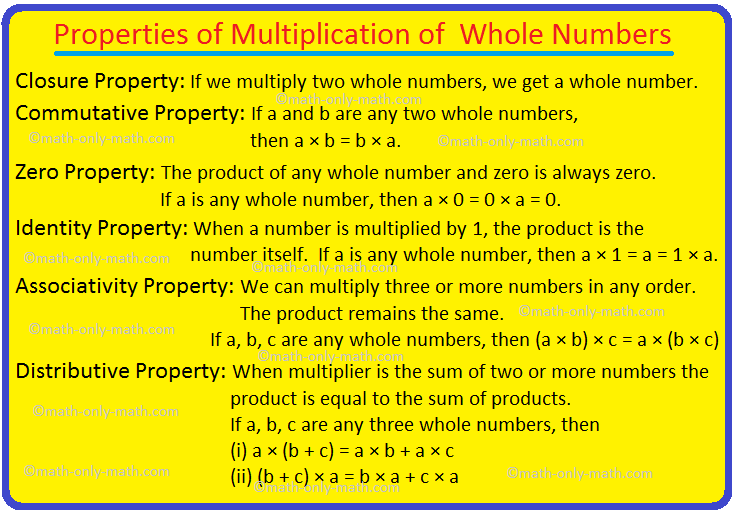
Properties of Multiplication | Multiplicative Identity | Whole Numbers
Jan 15, 25 12:08 AM
There are six properties of multiplication of whole numbers that will help to solve the problems easily. The six properties of multiplication are Closure Property, Commutative Property, Zero Property… -
Multiplication Table | Learn Tables from 0 – 25 | Multiplication Table
Jan 14, 25 11:53 PM
In math multiplication table we will learn the tables from 0 – 25. These multiplication tables help the students to learn the essential multiplication facts. Multiplication tables are very important f… -
3rd Grade Math Worksheets |3rd Grade Math Sheets|3rd Grade Math Lesson
Jan 14, 25 11:02 PM
3rd grade math worksheets is carefully planned and thoughtfully presented on mathematics for the students. Teachers and parents can also follow the worksheets to guide the students. -
3rd Grade Subtraction Worksheet | 3-Digit Subtraction Worksheets | Ans
Jan 14, 25 01:57 PM
In 3th Grade Addition Worksheet we will solve how to subtract 3-digit numbers by expansion, subtraction of 3-digit numbers without regrouping, subtraction of 3-digit numbers with regrouping, propertie… -
Facts about Subtraction | Subtraction of Small Numbers|Solved Examples
Jan 14, 25 12:29 AM
The operation to finding the difference between two numbers is called subtraction. Let us know some facts about subtraction which will help us to learn subtraction of large numbers. 1. Subtraction wit…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.