Standard Equation of a Parabola
We will discuss about the standard equation of a parabola.
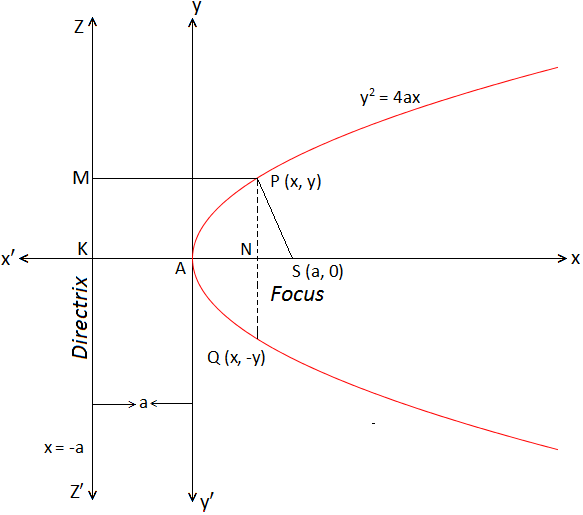
Let S be the focus and the straight line ZZ', the directrix of the required parabola. Let SK be the straight line through S perpendicular to the directrix, bisect SK at A and K being the point of intersection with the directrix.
Then
AS = AK
⇒ Distance of A from the focus = Distance of A from the directrix
⇒ A lies on the parabola
Let SK = 2a, where, a > 0.
Then AS = AK = a.
If this line SK intersects the parabola
at A then SK is the axis and A is the vertex of the
parabola. Draw the straight line AY through A
perpendicular to the axis. Now, we choose the origin of co-ordinates at A and x
and y-axis along AS and AY respectively.
Let P (x, y) be any point on the required parabola. Join SP and draw PM and PN perpendicular to the directrix ZZ' and x-axis. Then,
PM = NK = AN + AK = x + a
Now, P lies on the parabola ⇒ SP = PM
⇒ SP2 = PM2
⇒ (x – a)2 + (y – 0)2 = (x + a)2
⇒ y2 = 4ax, which is the required equation of the parabola. The equation of a parabola in the form y2 = 4ax is known as the standard equation of a parabola.
Notes:
(i) The parabola has two real foci situated on its axis one of which is the focus S and the other lies at infinity. The corresponding directrix is also at infinity.
(ii) The vertex of the parabola y2 = 4ax is at the origin i.e., the co-ordinates of its vertex are (0, 0).
(iii) The co-ordinates of the focus S of the parabola y2 = 4ax are (a, 0).
(iv) The axis of the parabola y2 = 4ax is positive x-axis (assuming a> 0).
(v) The parabola is
symmetric with respect to with respect to its axis. If the point P(x, y) lies on the parabola y2 = 4ax
with respect to x-axis, then the point Q (x, -y) also lies on it.
(vi) We have, y2 = 0 when x = 0; hence, the straight line x = 0 (i.e., y-axis) intersects the parabola y2 = 4ax at coincident points. Therefore, y-axis is a tangent to the parabola y2 = 4ax at the origin.
(vii) The line segment PQ is the double ordinate of P and PQ = 2y.
(viii) The co-ordinates of the end points of the latus rectum L1L2 of the parabola y2 = 4ax are (a, 2a) and (a, -2a) respectively
(ix) The length of the latus rectum of the parabola y2 = 4ax is 4a.
(ix) The equation of the directrix of the parabola y2 = 4ax is x = - a ⇒ x + a = 0.
(x) The directrix of the parabola y2 = 4ax is parallel to y-axis and it passes through the point K (- a, 0).
(xi) x = at2, y = 2at is the parametric form of the parabola y2 = 4ax and t is called the parameter.
(xii) The co-ordinates of any point on the parabola y2 = 4ax can be represented as (at2, 2at) where (at2, 2at) are called the parametric co-ordinates of a point on the parabola y2 = 4ax.
(xiii) From the standard equation of the parabola y2 = 4ax we see that the value of y becomes imaginary when x < 0. Therefore, no portion of the parabola y2 = 4ax lies to the left of y-axis.
Again, if x is positive and gradually increases then y also increases and for each positive value of x we get two values of y which are equal and opposite in signs. Therefore, the curve extends to infinity on the right of the y-axis.
● The Parabola
- Concept of Parabola
- Standard Equation of a Parabola
- Standard form of Parabola y22 = - 4ax
- Standard form of Parabola x22 = 4ay
- Standard form of Parabola x22 = -4ay
- Parabola whose Vertex at a given Point and Axis is Parallel to x-axis
- Parabola whose Vertex at a given Point and Axis is Parallel to y-axis
- Position of a Point with respect to a Parabola
- Parametric Equations of a Parabola
- Parabola Formulae
- Problems on Parabola
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Standard Equation of a Parabola to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
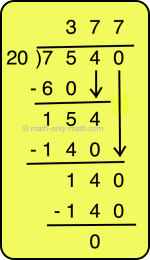
How to Do Long Division? | Method | Steps | Examples | Worksheets |Ans
Apr 20, 25 11:46 AM
As we know that the division is to distribute a given value or quantity into groups having equal values. In long division, values at the individual place (Thousands, Hundreds, Tens, Ones) are dividend… -
Word Problems on Division | Examples on Word Problems on Division
Apr 20, 25 11:17 AM
Word problems on division for fourth grade students are solved here step by step. Consider the following examples on word problems involving division: 1. $5,876 are distributed equally among 26 men. H… -
Subtraction of 4-Digit Numbers | Subtract Numbers with Four Digit
Apr 20, 25 10:27 AM
We will learn about the subtraction of 4-digit numbers (without borrowing and with borrowing). We know when one number is subtracted from another number the result obtained is called the difference. -
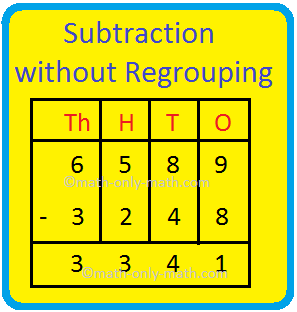
Subtraction without Regrouping |4-Digit, 5-Digit & 6-Digit Subtraction
Apr 20, 25 10:25 AM
We will learn subtracting 4-digit, 5-digit and 6-digit numbers without regrouping. We first arrange the numbers one below the other in place value columns and then subtract the digits under each colum… -
Worksheets on Missing Numbers from 1 to 20 | Counting Missing Numbers
Apr 20, 25 10:17 AM
Printable worksheets on missing numbers from 1 to 20 help the kids to practice counting of the numbers.




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.