Standard Equation of an Hyperbola
We will learn how to find the standard equation of a hyperbola.
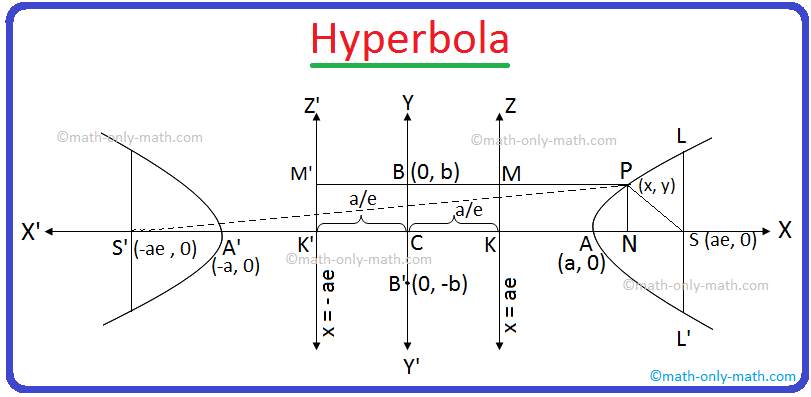
Let S be the focus, e (> 1) be the eccentricity and line KZ its directrix of the hyperbola whose equation is required.
From the point S draw SK perpendicular to the directrix KZ. The line segment SK and the produced SK divides internally at A and externally at A’ respectively in the ratio e : 1.
Then,
SAAK = e : 1
⇒ SA = e ∙ AK …………. (ii)
and SA′A′K = e : 1
⇒ SA' = e ∙ A'K …………………. (ii)
The points A and A' he on the required hyperbola because
according to the definition of hyperbola A and A’are such points that their
distance from the focus bear constant ratio e (>1) to their respective
distance from the directrix, therefore A and A' he on the required hyperbola.
Let AA’ = 2a and C be the mid-point of the line segment AA'. Therefore, CA = CA' = a.
Now draw CY perpendicular to AA’ and mark the origin at C. CX and CY are assumed as x and y-axes respectively.
Now, adding the above two equations (i) and (ii) we have,
SA + SA' = e (AK + A'K)
⇒ CS - CA + CS + CA' = e (AC - CK + A’C + CK)
⇒ CS - CA + CS + CA' = e (AC - CK + A’C + CK)
Now put the value of CA = CA' = a.
⇒ CS - a + CS + a = e (a - CK + a + CK)
⇒2CS = e (2a)
⇒ 2CS = 2ae
⇒ CS = ae …………………… (iii)
Now, again subtracting above two equations (i) from (ii) we have,
⇒ SA' - SA = e (A'K - AK)
⇒ AA'= e {(CA’ + CK) - (CA - CK)}
⇒ AA' = e (CA’ + CK - CA + CK)
Now put the value of CA = CA' = a.
⇒ AA' = e (a + CK - a + CK)
⇒ 2a = e (2CK)
⇒ 2a = 2e (CK)
⇒ a = e (CK)
⇒ CK = ae ………………. (iv)
Let P (x, y) be any point on the required hyperbola and from P draw PM and PN perpendicular to KZ and KX respectively. Now join SP.
According to the graph, CN = x and PN = y.
Now form the definition of hyperbola we get,
SP = e ∙ PM
⇒ Sp2= e2PM2
⇒ SP2 = e2KN2
⇒ SP2 = e2(CN - CK)2
⇒ (x - ae)2 + y2 = e2(x - ae)2, [From (iii) and (iv)]
⇒ x2 - 2aex + (ae)2 + y2 = (ex - a)2
⇒ (ex)2 - 2aex + a2 = x2 - 2aex + (ae)2 + y2
⇒ (ex)2 - x2 - y2 = (ae)2 - a2
⇒ x2(e2 - 1) - y2 = a2(e2 - 1)
⇒ x2a2 - y2a2(e2−1) = 1
We know that a2(e2 - 1) = b2
Therefore, x2a2 - y2b2 = 1
For all the points P (x, y) the relation x2a2 - y2b2 = 1 satisfies on the required hyperbola.
Therefore, the equation x2a2 - y2b2 = 1 represents the equation of the hyperbola.
The equation of a hyperbola in the form of x2a2 - y2b2 = 1 is known as the standard equation of the hyperbola.
● The Hyperbola
- Definition of Hyperbola
- Standard Equation of an Hyperbola
- Vertex of the Hyperbola
- Centre of the Hyperbola
- Transverse and Conjugate Axis of the Hyperbola
- Two Foci and Two Directrices of the Hyperbola
- Latus Rectum of the Hyperbola
- Position of a Point with Respect to the Hyperbola
- Conjugate Hyperbola
- Rectangular Hyperbola
- Parametric Equation of the Hyperbola
- Hyperbola Formulae
- Problems on Hyperbola
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Standard Equation of an Hyperbola to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
How to Do Long Division? | Method | Steps | Examples | Worksheets |Ans
Apr 20, 25 11:46 AM
As we know that the division is to distribute a given value or quantity into groups having equal values. In long division, values at the individual place (Thousands, Hundreds, Tens, Ones) are dividend… -
Word Problems on Division | Examples on Word Problems on Division
Apr 20, 25 11:17 AM
Word problems on division for fourth grade students are solved here step by step. Consider the following examples on word problems involving division: 1. $5,876 are distributed equally among 26 men. H… -
Subtraction of 4-Digit Numbers | Subtract Numbers with Four Digit
Apr 20, 25 10:27 AM
We will learn about the subtraction of 4-digit numbers (without borrowing and with borrowing). We know when one number is subtracted from another number the result obtained is called the difference. -
Subtraction without Regrouping |4-Digit, 5-Digit & 6-Digit Subtraction
Apr 20, 25 10:25 AM
We will learn subtracting 4-digit, 5-digit and 6-digit numbers without regrouping. We first arrange the numbers one below the other in place value columns and then subtract the digits under each colum… -
Worksheets on Missing Numbers from 1 to 20 | Counting Missing Numbers
Apr 20, 25 10:17 AM
Printable worksheets on missing numbers from 1 to 20 help the kids to practice counting of the numbers.




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.