Slope-intercept Form
We will learn how to find the slope-intercept form of a line.
The equation of a straight line with slope m and making an intercept b on y-axis is y = mx + b
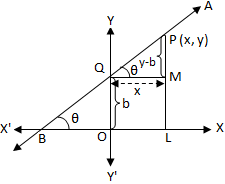
Let a line AB intersects the y-axis at Q and makes an angle θ with the positive direction of x-axis in anticlockwise sense and OQ = b.
Now we have to find the equation of the straight line AB.
Let P (x, y) be any point on the line AB. Draw PL perpendicular to x-axis and CM perpendicular on PL.
Clearly, <PQM = θ, Since, QM parallel to x-axis.
Since the co-ordinate of p is (x, y) hence, PL = y
PM = PL - ML = PL - OQ = y - b
Again, QM = OL = x
Now form the right angle ∆ PQM, we get,
tan θ = PM/QM = y - b/x
⇒ tan θ = y - b/x
If tan θ = m then we have,
m = y - b/x
⇒ y = mx + b, which is the required equation of the line and satisfied by the co-ordinates of all points on the line AB.
Solved examples on equation of a line in slope-intercept form:
1. Find the equation of a straight line whose slope = -7 and which intersects the y-axis at a distance of 2 units from the origin.
Solution:
Here m = -7 and b = 2. Therefore, the equation of the straight line is y = mx + b ⇒ y = -7x + 2 ⇒ 7x + y – 2 = 0.
2. Find the slope and y-intercept of the straight-line 4x - 7y + 1 = 0.
Solution:
The equation of the given straight line is
4x - 7y + 1 = 0
⇒ 7y = 4x + 1
⇒ y = 4/7x + 1/7
Now, compare the above equation with the equation y = mx + b we get,
m = 4/7 and b =1/7.
Therefore, the slope of the given straight line is 4/7 and its y-intercept = 1/7 units.
Notes:
(i) The equation of a straight line of the form y = mx + b is called its slope-intercept from.
(ii) If m and b are two fixed constants then equation of slope-intercept from y =mx + b represent a fixed line.
(iii) If m is a fixed constant and b is an arbitrary constant then equation of slope-intercept from y =mx + b represent a family of parallel straight lines.
(iv) If b is a fixed constant and m is an arbitrary constant then equation y = mx + b represent a family of straight lines passing through a fixed point.
(v) If m and c both are arbitrary constants the equation y =mx + b represents a variable line.
(vi) A line can cuts off an intercept b from the positive or negative y-axis then b is positive or negative respectively.
(vii) If the line passes through the origin, then 0 = 0m + b ⇒ b = 0. Therefore, the equation of a line passing through the origin is y = mx, where m is the slope of the line.
(viii) If the slope or gradient i.e., m = 0 and y-intercept i.e., b ≠ 0, then equation y = mx + b ⇒ y = 0x + b ⇒ y = b, which represents the equation of a line parallel to x-axis.
So, when m = 0 then the slope-intercept form y = mx + b can be expressed as an equation of a straight line parallel to x-axis.
(ix) When slope and y-intercept is zero (i.e., m = 0 and b = 0) then equation y =mx + b ⇒ y = 0x + 0 ⇒ y = 0, which represents the equation of x-axis.
So, when m = 0 and b = 0 then the slope-intercept form y = mx + b can be expressed as an equation of x-axis.
(x) When the angle of inclination θ = 90°, then slope m = tan 90° = undefined. In this case the line AB will be either parallel to y-axis or will coincide with the y-axis.
So, the slope-intercept form y = mx + b cannot be expressed as an equation of y-axis or the equation of a line parallel to y-axis.
● The Straight Line
- Straight Line
- Slope of a Straight Line
- Slope of a Line through Two Given Points
- Collinearity of Three Points
- Equation of a Line Parallel to x-axis
- Equation of a Line Parallel to y-axis
- Slope-intercept Form
- Point-slope Form
- Straight line in Two-point Form
- Straight Line in Intercept Form
- Straight Line in Normal Form
- General Form into Slope-intercept Form
- General Form into Intercept Form
- General Form into Normal Form
- Point of Intersection of Two Lines
- Concurrency of Three Lines
- Angle between Two Straight Lines
- Condition of Parallelism of Lines
- Equation of a Line Parallel to a Line
- Condition of Perpendicularity of Two Lines
- Equation of a Line Perpendicular to a Line
- Identical Straight Lines
- Position of a Point Relative to a Line
- Distance of a Point from a Straight Line
- Equations of the Bisectors of the Angles between Two Straight Lines
- Bisector of the Angle which Contains the Origin
- Straight Line Formulae
- Problems on Straight Lines
- Word Problems on Straight Lines
- Problems on Slope and Intercept
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Slope-intercept Form to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
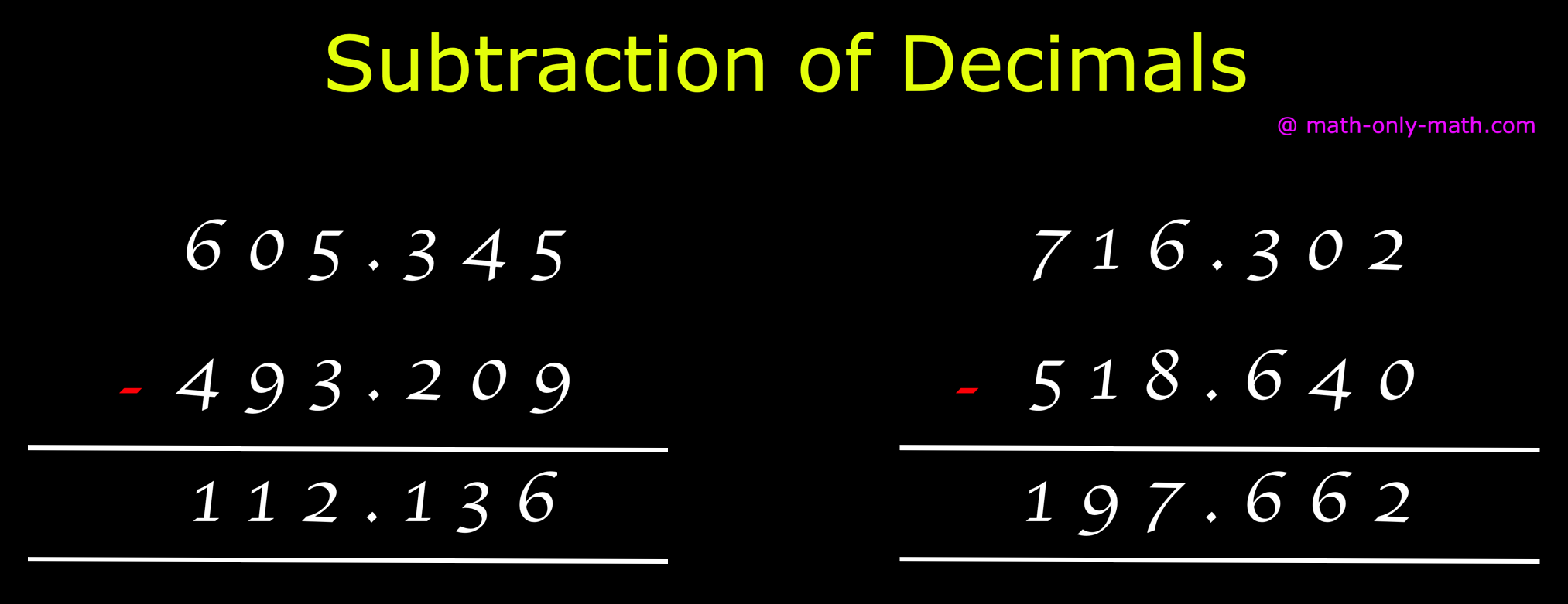
Subtraction of Decimals | Subtracting Decimals | Decimal Subtraction
Apr 24, 25 03:25 PM
We will discuss here about the subtraction of decimals. Decimals are subtracted in the same way as we subtract ordinary numbers. We arrange the digits in columns -
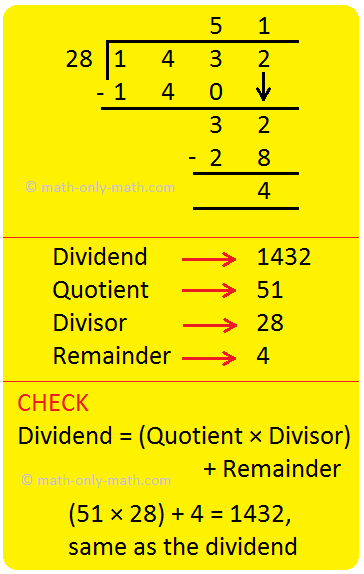
How to Do Long Division? | Method | Steps | Examples | Worksheets |Ans
Apr 24, 25 10:18 AM
As we know that the division is to distribute a given value or quantity into groups having equal values. In long division, values at the individual place (Thousands, Hundreds, Tens, Ones) are dividend… -
Division by Two-Digit Numbers | Knowledge of Estimation | Division
Apr 24, 25 10:12 AM
In division by two-digit numbers we will practice dividing two, three, four and five digits by two-digit numbers. Consider the following examples on division by two-digit numbers: Let us use our knowl… -
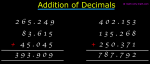
Addition of Decimals | How to Add Decimals? | Adding Decimals|Addition
Apr 24, 25 01:45 AM
We will discuss here about the addition of decimals. Decimals are added in the same way as we add ordinary numbers. We arrange the digits in columns and then add as required. Let us consider some -
Addition of Like Fractions | Examples | Videos | Worksheet | Fractions
Apr 23, 25 09:23 AM
To add two or more like fractions we simplify add their numerators. The denominator remains same. Thus, to add the fractions with the same denominator, we simply add their numerators and write the com…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.