Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Regular and Irregular Polygons
We will learn about different types of regular and irregular polygons and their properties.
Regular Polygons:
A polygon which has all its sides of equal length and all
its angles of equal measures is called a regular polygon.
Definition of Regular Polygons:
If all the sides and angles of a polygon are equal, then the polygon is called a regular polygon.
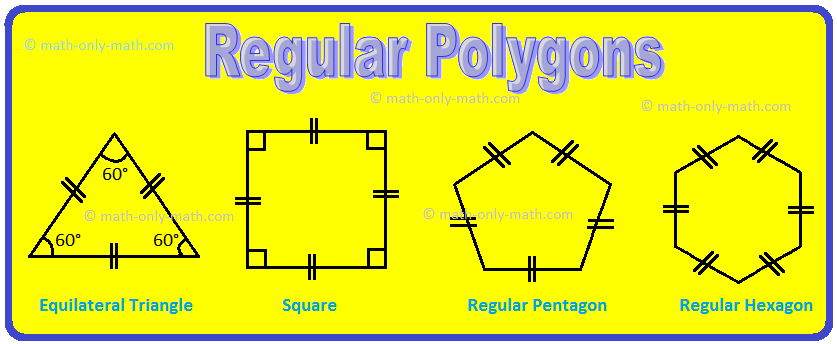
The following figures are regular polygons.
Examples of Regular Polygons:
|
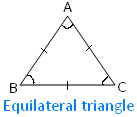
In the adjoining figure of an equilateral triangle ABC there
are three sides i.e., AB, BC and CA are equal and there are three angles i.e., ∠ABC, ∠BCA and ∠CAB are equal.
|
|
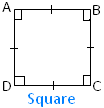
In the adjoining figure of a square ABCD there are four sides i.e., AB, BC, CD and DA are equal and there are four angles i.e., ∠ABC, ∠BCD, ∠CDA and ∠DAB are equal.
|
|
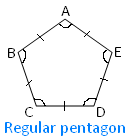
In the adjoining figure of a regular pentagon ABCDE there are five sides i.e., AB, BC, CD, DE and EA are equal and there are five angles i.e., ∠ABC, ∠BCD, ∠CDE, ∠DEA and ∠EAB are equal.
|
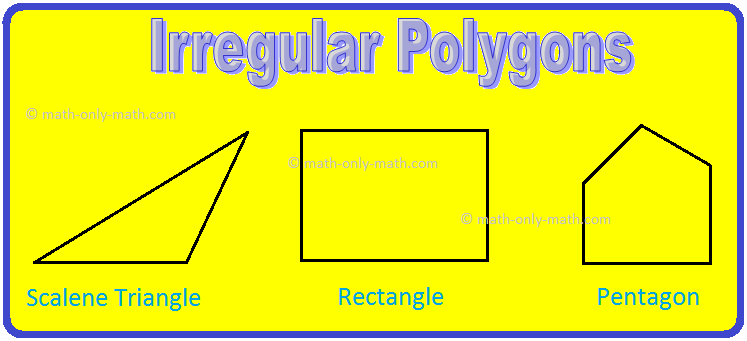
Irregular polygons (Non-Regular Polygons):
A polygon which has all its sides of unequal length and all
its angles of unequal measures is called an irregular polygon or non-regular polygons.
Definition of Irregular Polygons:
A polygons is called a non-regular or irregular polygon, if all the sides are not equal.
The following figures are irregular polygons.
Examples of Irregular Polygons:
|
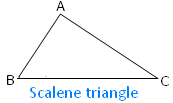
In the adjoining figure of a scalene triangle ABC there are three sides i.e., AB, BC and CA are unequal and there are three angles i.e., ∠ABC, ∠BCA and ∠CAB are unequal. Therefore, a scalene triangle is an irregular polygon. |
|
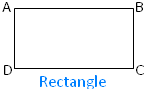
In the adjoining figure of a rectangle ABCD there are four sides i.e., AB, BC, CD and DA where the opposite sides are equal i.e., AB = CD and BC = AD. So, all the sides are not equal to each other.
Similarly, among the four angles i.e., ∠ABC, ∠BCD, ∠CDA and ∠DAB where the opposite angles are equal i.e., ∠ABC = ∠CDA and ∠BCD = ∠DAB. So, all the angles are not equal to each other. Therefore, a square is an irregular polygon. |
|
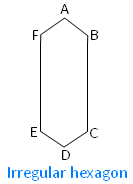
In the adjoining figure of an irregular hexagon ABCDEF there are six sides i.e., AB, BC, CD, DE, EF and FA are equal and there are six angles i.e., ∠ABC, ∠BCD, ∠CDE, ∠DEF, ∠EFA and ∠FAB are equal.
|
● Polygons
Polygon and its Classification
Interior and Exterior of the Polygon
Number of Triangles Contained in a Polygon
Angle Sum Property of a Polygon
Problems on Angle Sum Property of a Polygon
Sum of the Interior Angles of a Polygon
Sum of the Exterior Angles of a Polygon
7th Grade Math Problems
8th Grade Math Practice
From Regular and Irregular Polygon to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.