Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Angles
Angles are very important in our daily life so it’s very necessary to understand about angle.
Two rays meeting at a common endpoint form an angle.
Definition of Angles:
When two rays have a common initial point, an angle is formed.
The common initial point is called the vertex of the angles, and the two rays forming the angle are called the arms of sides of the angle.
An angle is represented by the symbol '∠'.
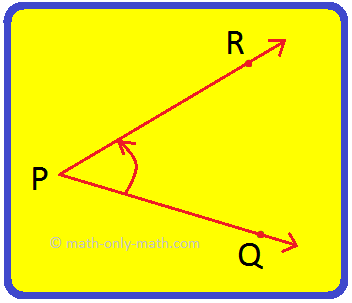
In the adjoining figure, two rays AB and BC are called the arms of the angle ABC.
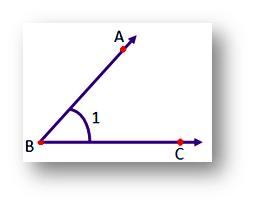
Common endpoint B is called the vertex of the angle.
We can name the angle as ∠ABC, ∠B or ∠1.
The symbol for denoting an angle is ∠.
In naming an angle, the vertex is always written in the middle. We can also name an angle by simply writing its vertex.
For example, ∠QPR or ∠RPQ can be denoted as ∠P.
In case two or more than two angles share the same vertex, it is not possible to denote them by the vertex only.
The unit for measuring an angle is degree and is denoted as °.
If there are more than 1 angles, we can label them as either ∠1, ∠2, ∠3, ∠4 or ∠ABC, ∠CBD, ∠DBE, ∠EBF.
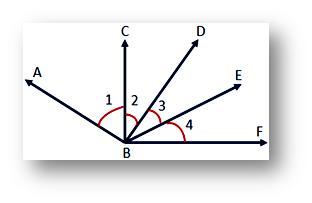
We use a protractor to measure the angles.
Working Rules to Form an Angle:
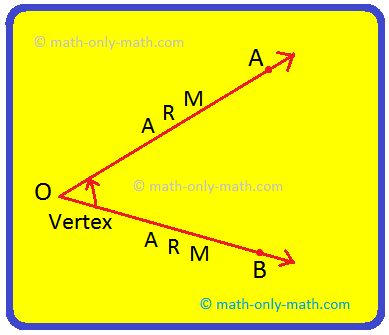
Step I: Draw two rays starting from the same initial point O
Step II: Name them as \(\overleftrightarrow{OA}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{OB}\). These rays are arms or sides of the angle.
Step III: An angle will be formed with O as vertex of the angle. The symbol '∠' is used to denote an angle and write the angle ∠AOB or ∠AOB or ∠BOA.
Magnitude of an Angle:
It is the amount of rotation through which one of the arms must be rotated about vertex to bring it to the position of the other.
We observe that ……..
∠2 has greater magnitude than ∠1.
∠3 has greater magnitude than ∠2.
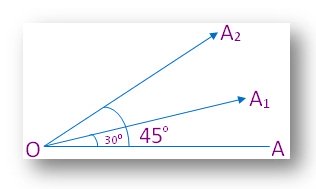
Note:
The more is the opening between the arms of the angles, the greater is the magnitude.
One complete rotation about a point is divided into 360 equal parts. Each part is called a degree and is written as 1° (one degree).
1° is further divided in 60 equal parts. Each part is called a minute and is written as 1' (one minute).
1' is further divided into 60 equal parts. Each part is called a second and is written as 1” (one second).
In general: 1° = 60’ = and 1’ = 60"
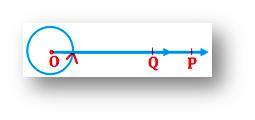
Measure of an angle:
The amount of turning which one arm must be turned about the vertex to bring it to the position of the other arm is called the measure of an angle.
In the figure ∠POQ, the measure of angle is written as m ∠POQ.
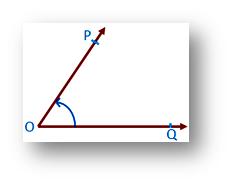
It shows that arm OQ is turned about the vertex O to bring it to OP.
One complete rotation about a point makes an angle of 360°.
1° = 60 minutes = 60'
1’ = 60 seconds = 60"
The instrument used for measuring an angle is a protractor.
● Lines and Angles
Fundamental Geometrical Concepts
Some Geometric Terms and Results
Complementary and Supplementary Angles
Parallel and Transversal Lines
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.