PEMDAS Rule
When all the four operations namely addition, subtraction, multiplication and division are involved in a problem, we perform the operations in the following sequence from left to right i.e. division, multiplication, addition and subtraction, remember the order as DMAS.
Easy
and simple way to remember PEMDAS rule!!
P → Parentheses first
E → Exponent (Powers, Square Roots, Cube Roots, etc.)
MD → Multiplication and Division (start from left to right)
AS → Addition and Subtraction (start from left to right)
Note:
(i) Start Multiply/Divide from left side to right side since they perform equally.
(ii) Start Add/Subtract from left side to right side since they perform equally.
Steps
to simplify the order of operation using PEMDAS rule:
First part of an equation is start solving inside the 'Parentheses'.
For
Example; (7 + 8) × 3
First solve inside ‘parentheses’ 7 + 8
= 15, then 15 × 3 = 45.
Next solve the mathematical 'Exponent'.
For Example; 32+ 5First solve ‘exponent’ part 32= 3 × 3 = 9, then 9 + 5 = 14.
Next,
the part of the equation is to calculate 'Multiplication' and 'Division'.
We know that, when division and multiplication follow one another, then their
order in that part of the equation is solved from left side to right side.
For
Example; 21 ÷ 7 × 12 ÷ 2
‘Multiplication’ and ‘Division’ perform equally, so calculate from left to right side. First solve 21 ÷ 7 = 3, then 3 × 12 = 36, then 36 ÷ 2 = 18.
In the last part of the equation is to calculate 'Addition' and 'Subtraction'. We know that, when addition and subtraction follow one another, then their order in that part of the equation is solved from left side to right side.
For
Example; 9 + 11 - 13 + 15
‘Addition’ and ‘Subtraction’ perform equally, so calculate from left to right side. First solve 9 + 11 = 20, then 20 - 13 = 7 and then 7 + 15 = 22.
These are simple rules need to be followed for simplifying or calculating using PEMDAS rule.
In brief, after we perform "P" and "E", start from left side to right side by solving any "M" or "D" as we find them. Then start from left side to right side solving any "A" or "S" as we find them.
Solved Examples using PEMDAS Rule:
1. 225 ÷ 15 + 14 × 5 – 128 ÷ 16 + 25
Solution:
First we carry out the divisions (colored in red)
225 ÷ 15 + 14 × 5 – 128 ÷ 16 + 25
15 + 14 × 5 – 8 + 25
Next, we multiply (colored in green)
15 + 14 × 5 – 8 + 25
15 + 70 – 8 + 25
Now, we will workout addition (colored in blue)
15 + 70 – 8 + 25
15 + 70 + 25 – 8
110 – 8
And then finally subtraction (colored in yellow)
110 – 8 = 102
Thus, 225 ÷ 15 + 14 × 5 – 128 ÷ 16 + 25 = 102
Simplify and find the answers using PEMDAS Rule:
1. (i) 14 + 8 ÷ 2 - 10
(ii) 13 × 3 – 42 ÷ 6
(iii) 40 ÷ 1 × 15 – 15
(iv) 667248 – 245631 + 1192311
(v) 7742859 + 65500 × 2000
(vi) 7188421 × 20 – 11199999
(vii) 1000 – 6 × 50 + 18 ÷ 6
(viii) 800 + 299 ÷ 299
(ix) 6020 × 5 – 8000 + 2999
(x) 7999 – 2463 ÷ 1 + 3001
Answers:
(i) 8
(ii) 32
(iii) 585
(iv) 1613928
(v) 138742859
(vi) 132568421
(vii) 703
(viii) 801
(ix) 25099
(x) 8537
● Related Concept
● Decimals
● Conversion of Unlike Decimals to Like Decimals
● Decimal and Fractional Expansion
● Converting Decimals to Fractions
● Converting Fractions to Decimals
● H.C.F. and L.C.M. of Decimals
● Repeating or Recurring Decimal
● BODMAS/PEMDAS Rules - Involving Decimals
● PEMDAS Rules - Involving Integers
● PEMDAS Rules - Involving Decimals
● BODMAS Rules - Involving Integers
● Conversion of Pure Recurring Decimal into Vulgar Fraction
● Conversion of Mixed Recurring Decimals into Vulgar Fractions
From PEMDAS Rules to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
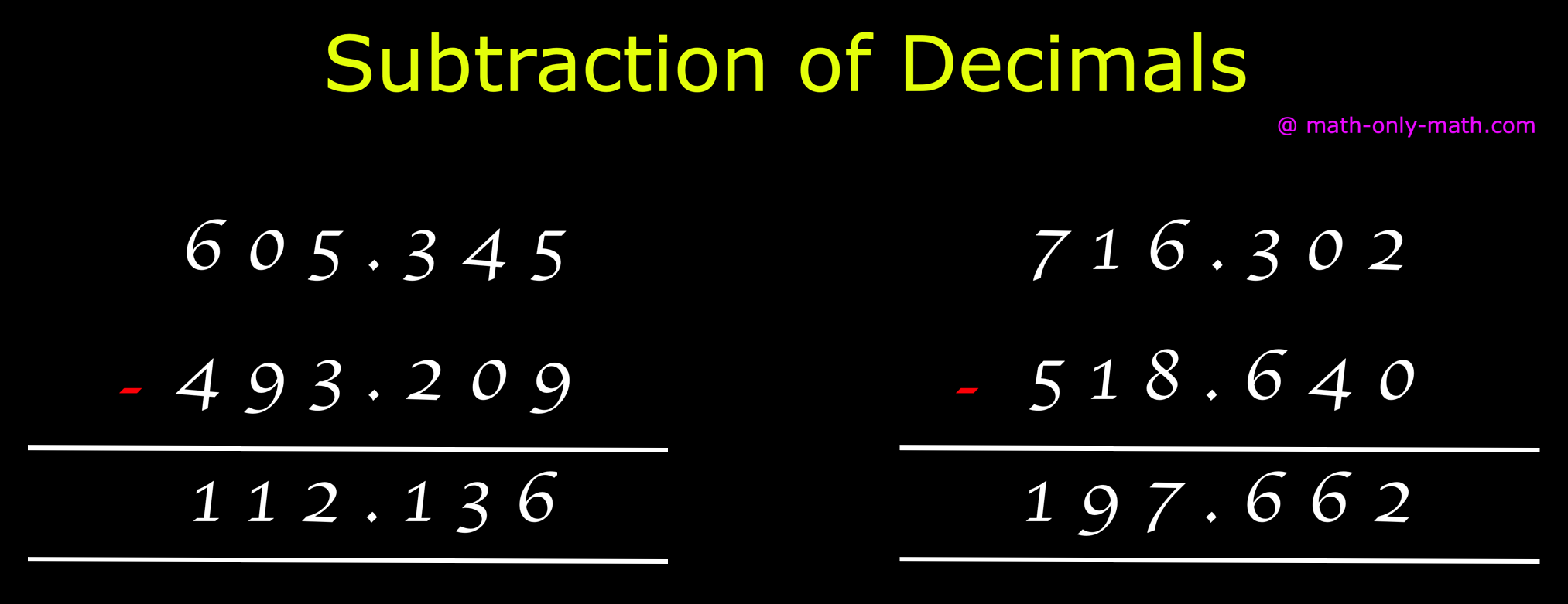
Subtraction of Decimals | Subtracting Decimals | Decimal Subtraction
Apr 24, 25 03:25 PM
We will discuss here about the subtraction of decimals. Decimals are subtracted in the same way as we subtract ordinary numbers. We arrange the digits in columns -
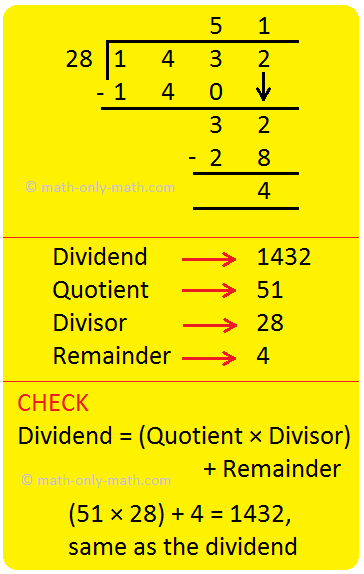
How to Do Long Division? | Method | Steps | Examples | Worksheets |Ans
Apr 24, 25 10:18 AM
As we know that the division is to distribute a given value or quantity into groups having equal values. In long division, values at the individual place (Thousands, Hundreds, Tens, Ones) are dividend… -
Division by Two-Digit Numbers | Knowledge of Estimation | Division
Apr 24, 25 10:12 AM
In division by two-digit numbers we will practice dividing two, three, four and five digits by two-digit numbers. Consider the following examples on division by two-digit numbers: Let us use our knowl… -
Addition of Decimals | How to Add Decimals? | Adding Decimals|Addition
Apr 24, 25 01:45 AM
We will discuss here about the addition of decimals. Decimals are added in the same way as we add ordinary numbers. We arrange the digits in columns and then add as required. Let us consider some -
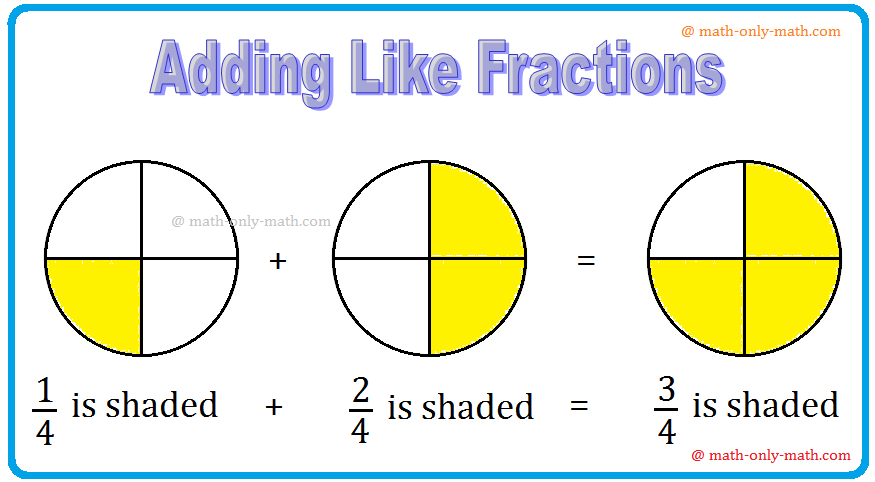
Addition of Like Fractions | Examples | Videos | Worksheet | Fractions
Apr 23, 25 09:23 AM
To add two or more like fractions we simplify add their numerators. The denominator remains same. Thus, to add the fractions with the same denominator, we simply add their numerators and write the com…


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.