Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Division of Two-Digit by a
One-Digit Numbers
In division of two-digit by a one-digit numbers are discussed here step by step.
How to divide 2-digit numbers by single-digit numbers?
Let us follow the examples to learn to divide 2-digit numbers by one-digit numbers.
Division of Two-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers Video
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
A: Dividing a 2-digit Number by a 1-Digit Number without Remainder:
Division of Smaller Numbers
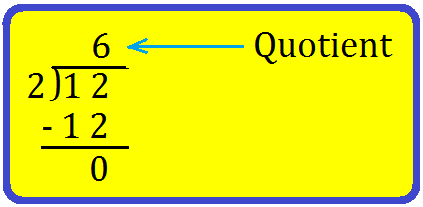
1. Let us divide 12 by 2.
Write 12 and 2 at the correct places as shown here.
Step I: Recall the table of the divisor 2 till you get the dividend 12.
1 × 2 = 2
2 × 2 = 4
3 × 2 = 6
4 × 2 = 8
5 × 2 = 10
6 × 2 = 12
Step II: Since 6 × 2 = 12 write 6 at the top and 12 below the dividend as shown.
Step III: Subtract 12 from 12. You will get 0.
So, 6 is the quotient.
2. Divide the following and verify the result
(i) 42 ÷ 6
(ii) 85 ÷ 5
Solution:
(i) 42 ÷ 6
Since, 6 sevens are 42, i.e., 6 × 7 = 42
So, 7 will be quotient
6 × 7 + 0 = 42, the dividend
So, quotient 7 is verified
Therefore, 7 is quotient
(ii) 85 ÷ 5
(a) 8 > 5 so first 8 will be divided. 8T ÷ 5 = 1T so quotient will be 1 ten
(b) 8T - 5T = 3T, 3T + 5 = 35 for 35 ÷ 5, 5 × 7 = 35.
So 7 is quotient
(c) 5 × 17 = 85 (dividend)
So, result is verified.
Therefore, Quotient = 17, remainder = 0
Note: Unlike in addition, subtraction or multiplication, we start from the tens place in division.
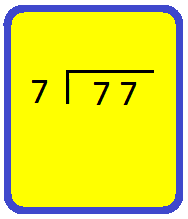
3. Divide 77 by 7
We proceed as follows:
Step I: Arrange the two given numbers as shown.
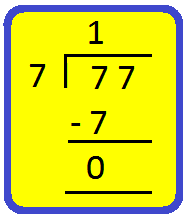
Step II: Divide the tens by 7.
We know 7 × 1 = 7.
Write 1 in tens place of the quotient and 7 below 7.
Subtract 7 from 7 to get 0.
Step III: Bring down 7 ones and divide it by 7.
We know 7 × 1 = 7.
Write 1 in the ones place of the quotient and 7 bellow 7.
Subtract 7 from 7 to get 0.
Thus, 77 ÷ 7 = 11
B: Dividing a 2-digit Number by a 1-Digit Number with Remainder:
Division of Smaller Numbers
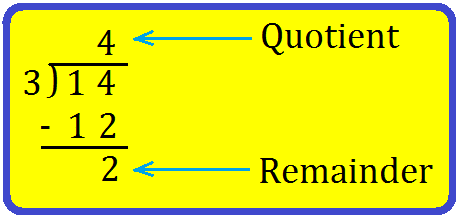
1. Let us now divide 14 by 3.
Write 14 and 3 at the correct places as shown.
Step I: Recall the table of the divisor 3, till you get the dividend 14.
1 × 3 = 3
2 × 3 = 6
3 × 3 = 9
4 × 3 = 12
5 × 3 = 15
Step II: We can see that 14 is not there in the table of 3. So, look for the number just smaller than 14 in the table. It is 12.
Step III: Since 4 × 3 = 12, write 4 at the top and 12 below the dividend.
Step IV: Subtract 12 from 14, you get 2.
Since 2 < 3 we cannot divide further.
So, 4 is the quotient and 2 is the remainder.
2. Divide the following and verify the result
76 ÷ 6
(a) 7 > 6, so 7T will be divided by 6,
6 one is 6, so 1T is quotient
(b) 7 – 6 = 1, 6 is carried down, so 16 will, be divided by 6.
6 twos are 12, 6 threes are 18, so quotient will be 2.
(c) 16 - 12 = 4 is the remainder
(d) 6 × 12 + 4 = 72 + 4 = 76 (dividend)
Therefore, result is verified.
The quotient = 12
Remainder = 4
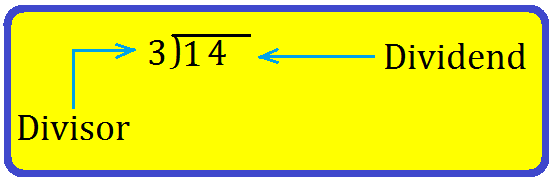
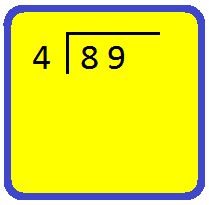
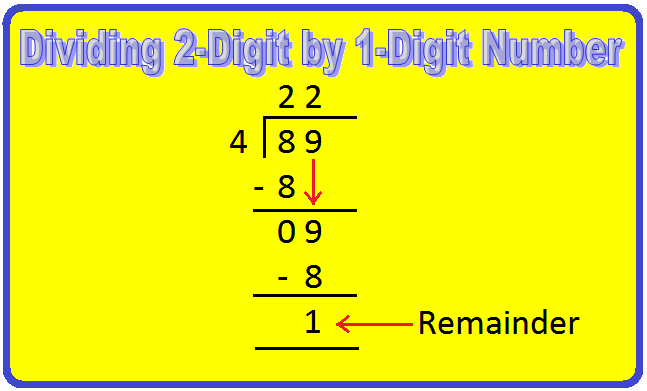
3. Divide 89 by 4.
We proceed as follows:
Step I: Arrange the two given numbers as shown.
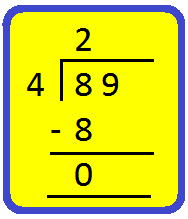
Step II: Divide the tens by 4.
Start by looking at the first number (tens place) in the dividend.
Find a number in the table of 4 less than or equal to 8
4 × 1 = 4,
4 × 2 = 8,
So, 2 is the required number.
4 × 2 = 8, write 2 in tens place of the quotient and 8 below 8.
Subtract the number you got by multiplying the divisor. from the number in the dividend.
Subtract 8 from 8 to get 0.
Step III: Divide the ones by 4.
Bring down the next digit (ones place), from the number in the dividend.
i.e., Bring down 9 ones and divide it by 4.
Repeat the same process again.
Find a number in the table of 4 less than or equal to 9
4 × 1 = 4,
4 × 2 = 8,
So, 2 is the required number.
4 × 2 = 8, write 2 in ones place of the quotient and 8 below 9.
Subtract 8 from 9 to get 1.
So, the quotient = 22 and remainder = 1.
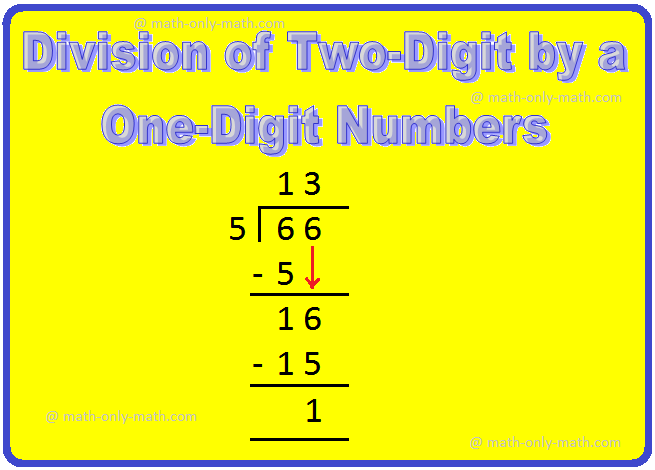
4. Divide 66 by 5 and verify the result.
We proceed as follows:
Step I: Arrange the two given numbers.
Step II: Divide the tens by 5.
Start by looking at the first number (tens place) in the dividend.
Find a number in the table of 5 less than or equal to 6
5 × 1 = 5,
So, 1 is the required number.
5 × 1 = 5, write 1 in tens place of the quotient and 5 below 6.
Subtract the number you got by multiplying the divisor. from the number in the dividend.
Subtract 5 from 6 to get 1.
Step III: Bring down the next digit (ones place), from the number in the dividend.
i.e., Bring down 6 ones
The number is 16
Now and divide 16 by 5.
Repeat the same process again.
Find a number in the table of 5 less than or equal to 16
5 × 1 = 5,
5 × 2 = 10,
5 × 3 = 15,
So, 3 is the required number.
5 × 3 = 15, write 3 in ones place of the quotient and 15 below 16.
Subtract 15 from 16 to get 1.
So, the quotient = 13 and remainder = 1.
So, 66 is dividend,
5 is divisor,
3 is quotient,
1 is remainder.
Check: Dividend = Quotient × Divisor - Remainder
= 13 × 5 + 1
= 65 + 1
= 66 = Dividend
The same method is used when dividing larger numbers.
Division of Greater Numbers:
In all the divisions of the previous section, the tens digit of the dividend is smaller than the divisor.
In this section, the tens digit of the dividend will either be equal to or greater than the divisor.
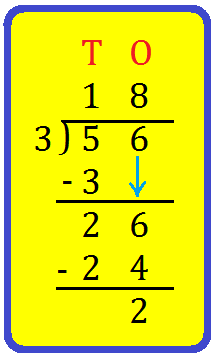
5. Let us divide 56 by 3.
Solution:
We see that the tens digit of the dividend '5' is greater than the divisor '3'.
Write 56 and 3 at the correct places.
Step I: Divide 5 tens by 3.
Recall the table of the divisor '3'. 1 × 3 = 3
5 tens ÷ 3 = 1 ten and 2 tens are left over.
Step II: Write 1 at the tens place of the quotient and 3 below 5 as shown.
Step III: Subtract 3 from 5, you get 2.
Step IV: Bring down the ones digit of the dividend '6'.
Divide 26 ones by 3.
Recall the table of the divisor 3'. 8 × 3 = 24
26 ones ÷ 3 = 8 ones and 2 ones are left over.
Step V: Write 8 at the ones place of the quotient and 24 below 26 as shown.
Step VI: Subtract 24 from 26, you get 2.
The quotient is 18 and the remainder is 2.
C. Word Problems on Dividing 2-Digit Number by 1-Digit Number
1. Nairitee's father buys 68 hibiscus plants. She plants them in 2 equal rows. How many plants are there in each row?
Solution:
First, we arrange the numbers as shown.
Divisor → 2 \(\overline{) 68 }\) ← Dividend
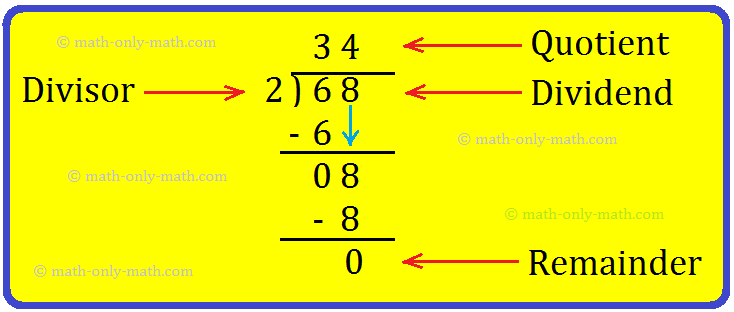
Step I: If the first digit of the dividend is bigger than the divisor, then start dividing tens.
6 tens ÷ 2 = 3 tens.
Write 3 in the tens place of the quotient and subtract 2 × 3 = 6 from 6.
6 - 6 = 0.
Step II: Bring down the ones digit, 8 and then divide ones.
8 ones ÷ 2 = 4 ones,
Write 4 in the ones place of the quotient and subtract 2 × 4 = 8 from 8.
8 - 8 = 0.
So, she plants 34 hibiscus plants in each row.
Worksheet on Division of Two-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers:
1. Find the quotient and the remainder, using long division method:
(i) 40 ÷ 4
(ii) 36 ÷ 6
(iii) 54 ÷ 6
(iv) 50 ÷ 9
(v) 63 ÷ 8
Answer:
1. (i) Quotient: 10; Remainder: 0
(ii) Quotient: 6 ; Remainder: 0
(iii) Quotient: 9 ; Remainder: 0
(iv) Quotient: 5 ; Remainder: 5
(v) Quotient: 7 ; Remainder: 7
2. Divide the following and check your answer using division algorithm:
(i) 46 ÷ 7
(ii) 89 ÷ 9
(iii) 65 ÷ 8
(iv) 35 ÷ 4
(v) 52 ÷ 6
Answer:
2. (i) Quotient: 6; Remainder: 4
(ii) Quotient: 9; Remainder: 8
(iii) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 1
(iv) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 3
(v) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 4
3. Divide the following:
(i) 89 ÷ 4
(ii) 99 ÷ 9
(iii) 92 ÷ 7
(iv) 82 ÷ 2
(v) 66 ÷ 6
(vi) 46 ÷ 7
(vii) 89 ÷ 9
(viii) 65 ÷ 8
(ix) 35 ÷ 4
(x) 52 ÷ 6
(xi) 46 ÷ 7
(xii) 89 ÷ 9
(xiii) 65 ÷ 8
(xiv) 35 ÷ 4
(xv) 52 ÷ 6
Answer:
3. (i) Quotient: 22; Remainder: 1
(ii) Quotient: 11; Remainder: 0
(iii) Quotient: 13; Remainder: 1
(iv) Quotient: 41; Remainder: 0
(v) Quotient: 11; Remainder: 0
(vi) Quotient: 6; Remainder: 4
(vii) Quotient: 9; Remainder: 8
(viii) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 1
(ix) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 3
(x) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 4
(xi) Quotient: 6; Remainder: 4
(xii) Quotient: 9; Remainder: 8
(xiii) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 1
(xiv) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 3
(xv) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 4
4. Divide and check your answer:
(i) 89 ÷ 8
(ii) 45 ÷ 2
(iii) 92 ÷ 3
(iv) 64 ÷ 4
(v) 88 ÷ 5
(vi) 55 ÷ 7
(vii) 65 ÷ 8
(viii) 61 ÷ 6
(ix) 82 ÷ 6
(x) 94 ÷ 6
Answer:
4. (i) Quotient: 11; Remainder: 1
(ii) Quotient: 22; Remainder: 1
(iii) Quotient: 30; Remainder: 2
(iv) Quotient: 16; Remainder: 0
(v) Quotient: 17; Remainder: 3
(vi) Quotient: 7; Remainder: 6
(vii) Quotient: 8; Remainder: 1
(viii) Quotient: 10; Remainder: 1
(ix) Quotient: 13; Remainder: 4
(x) Quotient: 15; Remainder: 4
5. Nairitee has fewer than 20 balloons.
She counted his balloons in fours. She has three left over.
She counted them in fives. She had four left over.
How many balloons does Nairitee have?
Answer:
5. 19 balloons
Related Concept
● Addition
● Check for Subtraction and Addition
● Word Problems Involving Addition and Subtraction
● Estimating Sums and Differences
● Multiply a Number by a 2-Digit Number
● Multiplication of a Number by a 3-Digit Number
● Word Problems on Multiplication
● Division of Two-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers
● Division of Four-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers
● Division by 10 and 100 and 1000
● Division by Two-Digit Numbers
From Division of Two-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
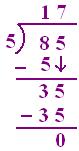

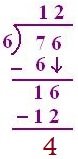


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.