Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Addition and Subtraction of Measuring Capacity
We will discuss about addition and subtraction of measuring capacity. The standard unit of measuring capacity is liter and the smaller unit is milliliter. The short way is to write liter as l and milliliter as ml. The liquid medicines are measured in ml. There are many types of vessels having capacity of 1 liter, 500 milliliter, 250 milliliter, etc,.
Containers or vessels meant to store different things like milk, sauce, mustard oil, etc., have different capacities. Therefore, the quantity of liquid a vessel can hold is its capacity.
Relationship between liter (l) and milliliter (ml):
We know one of the 1000 parts of a liter (l) is called a milliliter (ml).
So, 1 liter = 1000 milliliter
or, 1 l = 1000 ml
and, 1000 ml = 1 l
Addition of Units of Capacity:
Let us learn how to add different capacity measures. Here, litre and millilitre are arranged in different columns and then added like ordinary numbers.
For example:
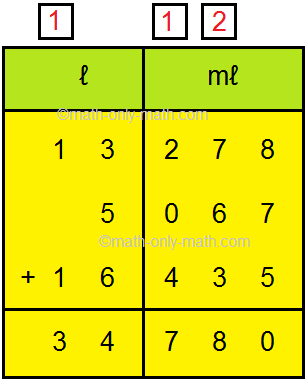
1. Add 13 ℓ 278 mℓ, 5 ℓ 67 mℓ and 16 ℓ 435 mℓ.
|
Solution: Let us add Step I: Arrange the numbers vertically. Step II: Write the capacities to be added in l and ml as shown here. Step III: First, add millilitres from right and then add the litres. |
Thus, 13 l 278 ml + 5 l 67 ml +16 l 435 ml = 34 l 780 ml
Word Problem on Addition of Capacity:
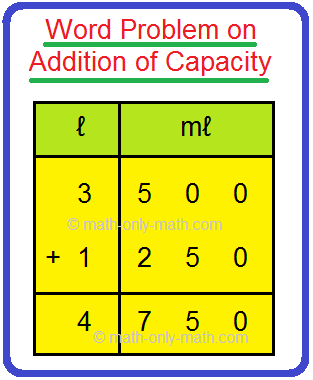
Samuel bought 3 ℓ 500 mℓ of milk in the morning and 1 ℓ 250 mℓ in the evening. How much milk Samuel bought in a day?
|
Solution: Milk bought in the morning = 3 ℓ 500 mℓ Milk bought in the evening = 1 ℓ 250 mℓ Total milk bought = 3 ℓ 500 mℓ + 1 ℓ 250 mℓ |
So, the total milk bought = 4 ℓ 750 mℓ
Subtraction of Units of Capacity:
Let us learn how to find the difference between capacities. Here, litre and millilitre are arranged in different columns and then subtract like ordinary numbers.
For example:
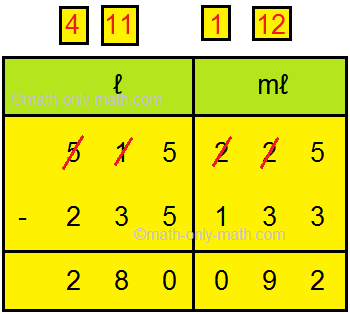
1. Subtract 235 l 133 ml and 515 l 225 ml
|
Solution: Let us subtract Step I: Arrange the numbers vertically. Step II: Write the capacities to be subtracted in l and ml as shown here. Step III: First, subtract millilitres from right and then subtract the litres. |
Thus, 515 l 225 ml - 235 l 133 ml = 280 l 92 ml
Word Problem on Subtraction of Capacity:
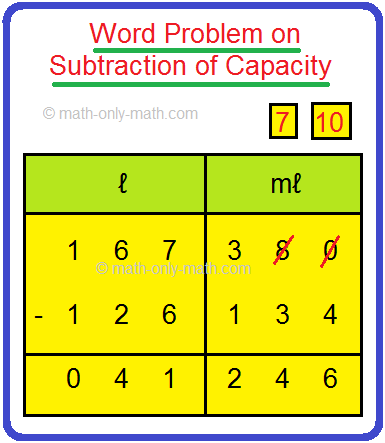
A tank is filled with 126 ℓ 134 mℓ oil. The capacity of tank is 167 ℓ 380 mℓ. How much more oil can be filled in it?
|
Solution: Capacity of tank = 167 ℓ 380 mℓ It is filled with oil = 126 ℓ 134 mℓ Oil can be filled = 167 ℓ 380 mℓ - 126 ℓ 134 mℓ |
So, the 41 ℓ 246 mℓ more oil can be filled in the tank.
Addition
and subtraction of measuring capacity in liters and milliliters:
1. (i) Add 525 ml and 275 ml
Solution:
525 ml
+ 275 ml
800 ml
(ii) Subtract 275 from 685 ml
Solution:
685 ml
- 275 ml
410 ml
2. A can holds 15 l and 500 ml of milk. Out of it 8 l and 350 ml milk is consumed. How much milk is left in the can now?
Solution:
Quantity of milk in the can = 15 l 500 ml
Quantity of milk consumed = 8 l 350 ml
Quantity of milk left = 15 l 500 ml - 8 l 350 ml
Thus, 15 l 500 ml 500 ml – 350 ml = 150 ml
- 8 l 350 ml 15 l – 8 l = 7 l
7 l 150 ml
Therefore, quantity of milk left = 7 l 150 ml
3. How much milk should be added to 12 l of milk to make it 16 l milk?
Solution:
Total milk should be = 16 l
Milk at present = - 12 l
Therefore, milk required = 4 l
From Addition and Subtraction of Measuring Capacity to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.