Volume and Surface Area of Cube and Cuboid
Here we will learn how to solve the problems on Volume and Surface Area of Cube and Cuboid:
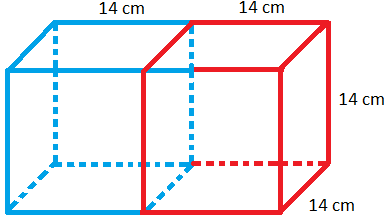
1. Two cubes of edge 14 cm each are joined end to end to form a cuboid. Find the volume and the total surface area of the cuboid.
Solution:
The volume of the cuboid = 2 × volume of one cube
= 2 × 143 cm3
= 5488 cm3
The total surface area of the cuboid = 2(28 × 14 + 14 × 14 + 14 × 28) cm2
= 2(28 + 14 + 28) × 14 cm2
= 2(2 × 14 + 1 × 14 + 2 × 14) × 14 cm2
= 2(2 + 1 + 2) × 14 × 14 cm2
= 2(5) × 14 × 14 cm2
= 10× 14 × 14 cm2
= 1960 cm2
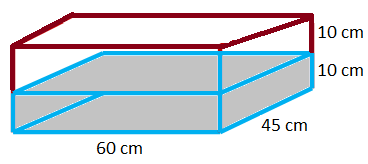
2. The dimensions of the base of a rectangular vessel are 60 cm × 45 cm. Its height is 20 cm. The vessel is half-filled with water. What should be the size of a solid iron cube which when dropped into the vessel will raise the water level up to the brim?
Solution:
The volume of the vessel = 60 × 45 × 20 cm3
= 54000 cm(^{3}\)
It is half-filled with water
So, the volume of the empty portion of the vessel = 12 × 54000 cm3
= 27000 cm3
The volume of the iron cube should be 27000 cm3 so that it displaces this amount of water and the water level comes up to the brim.
If the edge of the cube is x then,
x3 = 27000 cm3
⟹ x3 = (30)3 cm3
⟹ x = 30 cm
Therefore, the edge of the iron cube = 30 cm
The size of the cube should be 30 cm × 30 cm × 30 cm.
From Volume and Surface Area of Cube and Cuboid to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Counting Numbers from 1 to 50 | Match the Number | Missing Numbers
Apr 04, 25 03:46 PM
In counting numbers from 1 to 50, recognize the numbers, count and then join the numbers in the correct number order. Here we mainly need eye-hand coordination to draw the picture and maintain the num -
Counting Eleven to Twenty with Numbers and Words |Numbers from 11 - 20
Apr 04, 25 03:21 PM
Counting eleven to twenty with numbers and words are explained below. One ten and one more is eleven. Eleven comes after ten. One ten and two more is twelve. Twelve comes after eleven. -
5th Grade BODMAS Rule Worksheet | PEMDAS | Order of operations|Answers
Apr 03, 25 03:11 PM
In 5th Grade BODMAS Rule Worksheet you will get different types of problems on mathematical expressions involving different operations, mathematical expression with 'brackets' and 'of' and simplifying… -
Worksheet on Simplification | Simplify Expressions | BODMAS Questions
Apr 03, 25 02:58 PM
In worksheet on simplification, the questions are based in order to simplify expressions involving more than one bracket by using the steps of removal of brackets. This exercise sheet -
Divisible by 2 Video |Test of Divisibility by 2 Trick| Rules| Examples
Apr 03, 25 10:25 AM
A number is divisible by 2 if the digit at unit place is either 0 or multiple of 2. So a number is divisible by 2 if digit at its units place is 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8.




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.