Simple Math Formula on Trigonometry
Simple math formula on trigonometry is given in such an order that students can easily get the formula.
Trigonometry
● Measurement of Trigonometrical Angles:
(i) The angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc whose length is equal to the radius of the circle is called a radian.
(ii) A radian is a constant angle.
One radian = (2/π) rt. angle = 57°17’44.8” (approx.)
(iii) 1 rt. angle = 90° ; 1° = 60’ ; 1‘ = 60”.
(iv) 1 rt. angle = 100ᵍ ; 1ᵍ = 100’ ; 1‵ = 100‶.
(v) πᶜ 180° = 200ᵍ.
(vi) The circumference of a circle of radius r is 2πr where π is a constant; approximate value of π is ²²/₇; more accurate value of π is 3.14159 (approx.).
(vii) If Θ be the radian measure of an angle subtended at the centre of a circle of radius r by an arc of length s then Θ = ˢ/₀ or, s = rΘ.
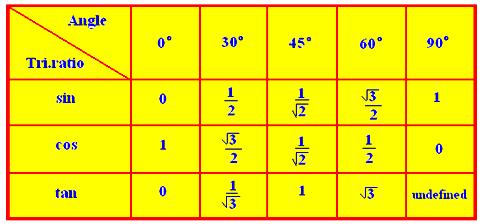
● Trigonometrical Ratios of some Standard Angles:
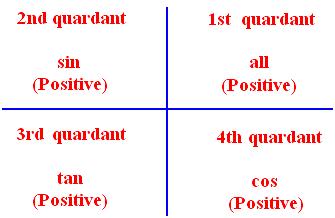
● Trigonometrical Ratios for Associated Angles:
(ii) If Θ is a positive acute angle and n is an even integer then,
(a) sin (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = sin Θ or, (- sin Θ)
(b) cos (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = cos Θ or, (- cos Θ)
(c) tan (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = tan Θ or, (- tan Θ).
(iii) If Θ is a positive acute angle and n is an odd integer then,
(a) sin (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = cos Θ or, (- cos Θ)
(b) cos (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = sin Θ or, (- sin Θ)
(c) tan (n ∙ 90° ± Θ) = cot ф or (- cot Θ).
● Compound Angles:
(i) sin (A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B.
(ii) sin ( A - B) = sin A cos B - cos A sin B.
(iii) cos (A + B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B.
(iv) cos (A - B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B.
(v) sin (A + B) sin (A - B) = sin² A - sin² B = cos² B - cos² A.
(vi) cos (A + B) cos (A - B) = cos² A - sin² B = cos² B - sin² A.
(vii) tan (A+ B) = (tan A + tan B)/(1 - tan A tan B).
(viii) tan (A - B) = (tan A - tan B)/(1 + tan A tan B).
(ix) cot (A + B) = (cot A cot B - 1)/(cot B + cot A).
(x) cot (A - B) = (cot A cot B + 1)/(cot B - cot A).
(xi) tan (A + B + C) = {(tan A + tan B + tan C) - (tan A tan B tan C)}/(1 - tan A tan B - tan B tan C - tan C tan A).
(xii) 2 sin A cos B = sin (A + B) + sin(A - B).
(xiii) 2 cos A sin B = sin (A + B ) - sin (A - B).
(xiv) 2 cos A cos B = cos (A + B ) + cos (A - B).
(xv) 2 sin A sin B = cos (A - B) - cos (A + B).
(xvii) sin C - sin D = 2 cos (C + D)/2 sin (C - D)/2.
(xviii) cos C + cos D = 2 cos (C + D)/2 cos (C - D)/2.
(xix) cos C - cos D = 2 sin (C + D)/2 sin (C - D)/2.
● Multiple Angles:
(i) sin 2Θ = 2 sin Θ cos Θ.
(ii) cos 2Θ = cos² Θ - sin² Θ.
(iii) cos 2 Θ = 2 cos² Θ - 1.
(iv) cos 2Θ = 1 - 2 sin² Θ.
(v) 1 - cos2Θ = 2 cos² Θ.
(vi) 1 - cos2Θ = 2 sin² Θ.
(vii) tan² Θ = (1 - cos 2Θ)/(1 + cos 2Θ).
(viii) sin 2Θ = (2 tan Θ)/(1 + tan² Θ)
(ix) cos 2Θ = (1 - tan² Θ)/(1 + tan² Θ).
(x) tan 2Θ = (2 tan Θ)/(1 - tan² Θ).
(xi) sin 3Θ = 3 sin Θ - 4 sin³ Θ.
(xii) cos 3ф = 4 cos³ Θ - 3 cos Θ.
(xiii) tan 3Θ = (3 tan Θ - tan³ Θ)/(1 - 3 tan² Θ).
● Submultiple Angles:
(i) sin Θ = 2 sin (Θ/2) cos (Θ/2).
(ii) cos Θ = cos² (Θ/2) - sin² (Θ/2).
(iii) cos Θ = 2 cos² (Θ/2) - 1.
(iv) cos ф = 1 - 2 sin² (Θ/2).
(v) 1 + cos Θ = 2 cos² (Θ/2).
(vi) 1 - cos Θ = 2 sin² (Θ/2).
(vii) tan² (Θ/2) = (1 - cos Θ)/(1 + cos Θ).
(viii) sin Θ = [2 tan (Θ/2)]/[1 + tan² (Θ/2)].
(ix) cos Θ = [1 - tan² (Θ/2)]/[1 + tan² (Θ/2)].
(x) tan Θ = [2 tan (Θ/2)]/[1 - tan² (Θ/2)].
(xi) sin Θ = 3 sin (Θ/3) - 4 sin³ (Θ/3).
(xii) cos Θ = 4 cos³ (Θ/3) - 3 cos (Θ/2).
(xiii) (a) sin 15° = cos 75° = (√3 - 1)/(2√2).
(b) cos 15° = sin 75° = (√3 + 1)/(2√2).
(c) tan 15° = 2 - √3.
(d) sin 22 ½° = √(2 - √2).
(e) cos 22 ½° = ½ [√(2 + √2)].
(f) tan 22 ½° = √2 - 1.
(g) sin 18 ° = (√5 - 1)/4 = cos 72°.
(h) cos 36° = cos 72° = (√5 + 1)/4.
(i) cos 18° = sin 72° = ¼ [√(10 + 2√5)].
(j) sin 36° = cos 54° = ¼ [√(10 - 2√5)].
● General Solutions:
(i) (a) If sin Θ = 0 then, Θ = nπ.
(b) If sin Θ = 1 then, Θ = (4n + 1)(π/2).
(c) If sin ф = -1 then, Θ = (4n - 1)(π/2).
(d) If sin Θ = sin α then, Θ = nπ + (-1)ⁿ α.
(ii) (a) If cos Θ = 0 then, Θ = (2n + 1)(π/2).
(b) If cos Θ = 1 then, Θ = 2nπ.
(c) If cos Θ = -1 then, Θ = (2n + 1)π.
(d) If cos Θ = cos α then, Θ = 2nπ ± α.
(ii) (a) If tan Θ = 0 then, Θ = nπ.
(b) If tan Θ = tan α then, Θ = 2nπ + α where, n = 0 or any integer.
● Inverse Circular Functions:
(i) sin (sin-1 x) = x ; cos (cos-1 x) = x ; tan (tan-1 x) = x.(ii) sin-1 (sin Θ) = Θ ; cos-1 (cos Θ) = Θ ; tan-1 (tan Θ) = Θ.
(iii) sin-1 x = cosec-1 (1/x) = cos-1 [√(1 - x2)] = sec-1 [1/√(1 - x2)]
= tan-1 [x/√(1 - x2)] = cot-1 [√(1 - x2)/x].
(iv) sin-1 x + cos-1 x = π/2 ; sec-1 x + cosec-1 x = π/2 ;
tan-1 x + cot-1 x = π/2.
(v) (a) tan-1 x + tan-1 y = tan-1 [(x + y)/(1 - xy)]
(b) tan-1 x - tan-1 y = tan-1 [(x - y)/(1 + xy)]
(vi) (a) sin-1 x + sin-1 y = sin-1 {x√(1 - y2) + y√(1 - x2)}
(b) sin-1 x - sin-1 y = sin-1 {x√(1 - y2 ) - y√(1 - x2)}
(vii) (a) cos-1 x + cos-1 y = cos-1 {xy - √(1 - x2) (1 - y2)}
(b) cos-1 x - cos-1 y = cos-1 {xy + √(1 - x2) (1 - y2)}.
(viii) 2 tan-1 x = sin-1 [2x/(1 + x2)] = cos-1 [(1 - x2)/(1 - x2)]
= tan-1 [2x/(1 - x2)].
(ix) tan-1 x + tan-1 y + tan-1 z = tan-1 [(x + y + z - xyz)/(1 - xy - yz - zx)]
(x) sin-1 x and cos-1 x are defined when -1 ≤ x ≤ 1 ; sec-1 x and cosec-1 x are defined when Ι x Ι ≥ 1 ; tan-1 x and cot-1 x are defined
when - ∞ < x < ∞.
(xi) If principal values of sin-1 x, cos-1 x and tan-1 x be α, β and γ respectively, then -π/2 ≤ α ≤ π/2, 0 ≤ β ≤ π and -π/2 ≤ γ ≤ π/2.
● Properties of Triangle:
(i) a/(sin A) = b/(sin B) = c/(sin C) = 2R.
(ii) a = b cos C + c cos B ; b = c cos A + a cos C ; c = a cos B + b cos A.
(iii) cos A = (b² + c² - a²)/2bc ; cos B = (c² + a² - b²)/2ca ;
cos C = (a² + b² - c²)/2ab
(iv) tan A = [(abc)/R] ∙[ 1/(b² + c² - a²)]
tan B = [(abc)/R] ∙ [1/(c² + a² - b²)]
tan C = [(abc)/R] ∙ [1/(a² + b² - c²)].
(v) sin (A/2) = √[(s - b) (s - c)/(bc)].
sin B/2 = √[(s - c) (s - a)/(ca)].
sin C/2 = √[(s - a) (s - b)/(ab)].
cos A/2 = √[s (s - a)/(bc)].
sin B/2 = √[s (s - b)/(ca)].
cos C/2 = √[s (s - c)/(ab)].
tan A/2 = √[(s - b) (s - c)/{s(s - c)}].
tan B/2 = √[(s - c) (s - a)/{s(s - b)}].
tan C/2 = √[(s - a) (s - b)/{s(s - c)}].
(vi) tan [(B - C)/2] = [(b - c)/(b + c)] cot (A/2).
tan [(C - A)/2] = [(c - a)/(c + a)] cot (B/2).
tan [(A - B)/2] = [(a - b)/(a + b)] cot (C/2).
(vii) ∆ = ½ [bc sin A] = ½ [ca sin B] = ½ [ab sin C].
(viii) ∆ = √{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)}.
(ix) R = ᵃᵇᶜ/₄₀.
(x) tan (A/2) = {(s - b)(s - c)}/∆.
tan (B/2) = {(s - c)(s - a)}/∆.
tan (C/2) = {(s - a)(s - b)}/∆
(xi) cot A/2 = {s(s - a)}/∆.
cot (B/2) = {s(s - b)}/∆.
cot (C/2) = {s(s - c)}/∆.
(xiii) r = ∆/s.
(xiv) r = 4R sin (A/2) sin (B/2) sin (C/2).
(xv) r = (s - a) tan (A/2) = (s - b) tan (B/2) = (s - c) tan (C/2).
(xvi) r₁ = ∆/(s - a) ; r₂ = ∆/(s - b); r₃ = ∆/(s - c) .
(xvii) r₁ = 4 R sin (A/2) cos (B/2) cos (C/2).
(xviii) r₂ = 4R sin (B/2) cos (C/2) cos (A/2).
(xix) r₃ = 4 R sin (C/2) cos (A/2) cos (B/2).
(xx) r₁ = s tan (A/2) ; r₂ = s tan (B/2) ; r₃ = s tan (C/2).
● Formula
- Basic Math Formulas
- Math Formula Sheet on Co-Ordinate Geometry
- All Math Formula on Mensuration
- Simple Math Formula on Trigonometry
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Simple Math Formula on Trigonometry to HOME PAGE
Recent Articles
-
Counting Numbers from 1 to 50 | Match the Number | Missing Numbers
Apr 04, 25 03:46 PM
In counting numbers from 1 to 50, recognize the numbers, count and then join the numbers in the correct number order. Here we mainly need eye-hand coordination to draw the picture and maintain the num -
Counting Eleven to Twenty with Numbers and Words |Numbers from 11 - 20
Apr 04, 25 03:21 PM
Counting eleven to twenty with numbers and words are explained below. One ten and one more is eleven. Eleven comes after ten. One ten and two more is twelve. Twelve comes after eleven. -
5th Grade BODMAS Rule Worksheet | PEMDAS | Order of operations|Answers
Apr 03, 25 03:11 PM
In 5th Grade BODMAS Rule Worksheet you will get different types of problems on mathematical expressions involving different operations, mathematical expression with 'brackets' and 'of' and simplifying… -
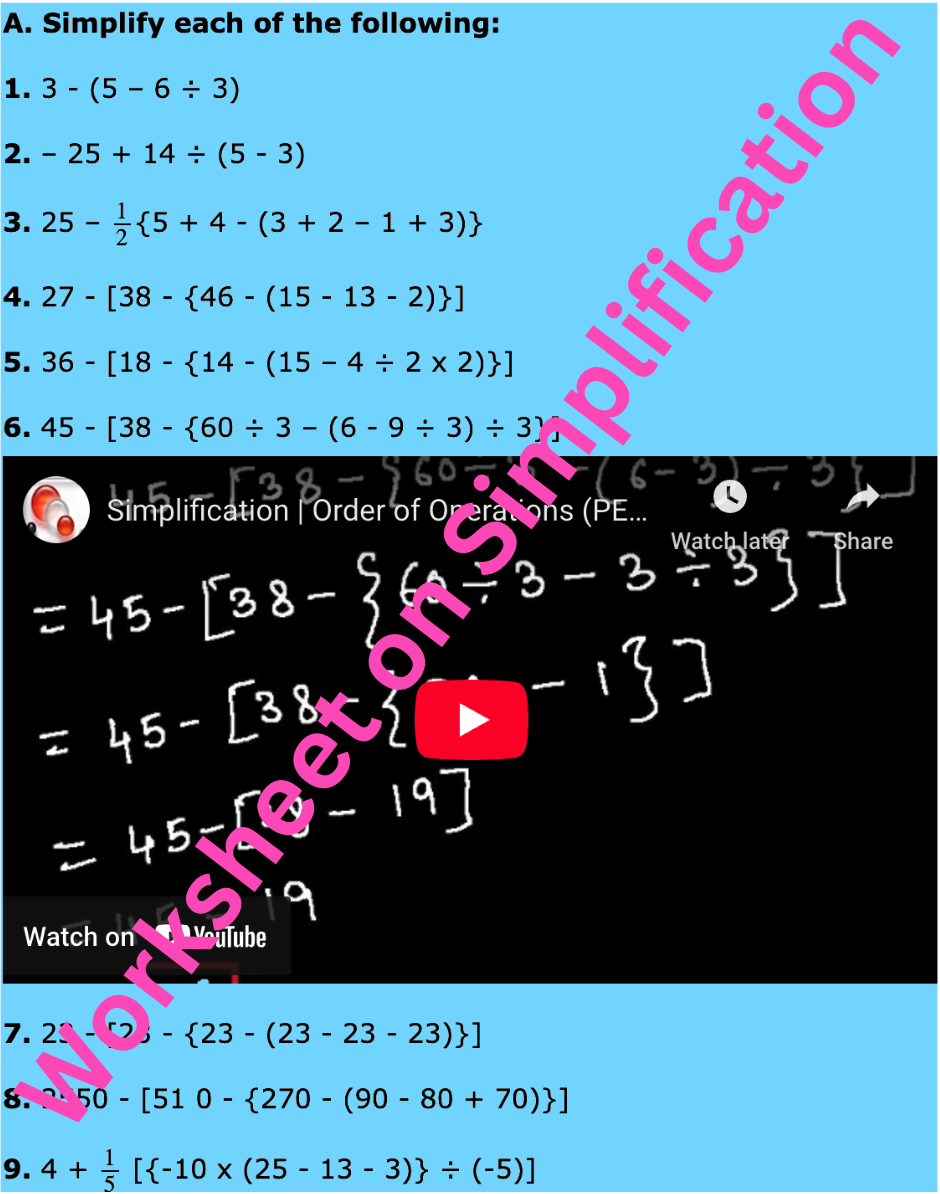
Worksheet on Simplification | Simplify Expressions | BODMAS Questions
Apr 03, 25 02:58 PM
In worksheet on simplification, the questions are based in order to simplify expressions involving more than one bracket by using the steps of removal of brackets. This exercise sheet -
Divisible by 2 Video |Test of Divisibility by 2 Trick| Rules| Examples
Apr 03, 25 10:25 AM
A number is divisible by 2 if the digit at unit place is either 0 or multiple of 2. So a number is divisible by 2 if digit at its units place is 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8.




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.