Set Theory
The set theory was developed by George Cantor in 1845-1918. Today, it is used in almost every branch of mathematics and serves as a fundamental part of present-day mathematics.
In set theory we will learn about representation in roster form and set builder form , types of sets (Empty set, singleton set, finite and infinite sets, equal and equivalent sets), cardinal number of a set, subsets (Proper subset, super set, power set), number of proper subsets, universal set, operation on sets (Union, intersection, difference and complement of sets).
In everyday life, we often talk of the collection of objects such as a bunch of keys, flock of birds, pack of cards, etc. In mathematics, we come across collections like natural numbers, whole numbers, prime and composite numbers.
Let us examine the following collections:
● Even natural numbers less than 20, i.e., 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18.
● Vowels in the English alphabet, i.e., a, e, i, o, u.
● Prime factors of 30 i.e. 2, 3, 5.
● Triangles on the basis of sides, i.e., equilateral, isosceles and scalene.
We observe that these examples are well-defined collections of objects.
Let us examine some more collections.
● Five most renowned scientists of the world.
● Seven most beautiful girls in a society.
● Three best surgeons in America.
These
examples are not well-defined collections of objects because the
criterion for determining as most renowned, most beautiful, best, varies
from person to person.
Sets:
A set is a well-defined collection of distinct objects.
We assume that,
● The word set is synonymous with the word collection, aggregate, class and comprises of elements.
● Objects, elements and members of a set are synonymous terms.
● Sets are usually denoted by capital letters A, B, C, ....., etc.
● Elements of the set are represented by small letters a, b, c, ....., etc.
If
‘a’ is an element of set A, then we say that ‘a’ belongs to A. We
denote the phrase ‘belongs to’ by the Greek symbol ‘∈‘ (epsilon). Thus,
we say that a ∈ A.
If ‘b’ is an element which does not belong to A, we represent this as b ∉ A.
Some important sets used in mathematics are
N: the set of all natural numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, .....}
Z: the set of all integers = {....., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, .....}
Q: the set of all rational numbers
R: the set of all real numbers
Z+: the set of all positive integers
W: the set of all whole numbers
● Set Theory
● Finite Sets and Infinite Sets
● Problems on Intersection of Sets
● Problems on Complement of a Set
● Problems on Operation on Sets
● Venn Diagrams in Different Situations
● Relationship in Sets using Venn Diagram
● Union of Sets using Venn Diagram
● Intersection of Sets using Venn Diagram
● Disjoint of Sets using Venn Diagram
● Difference of Sets using Venn Diagram
8th Grade Math Practice
From Set Theory to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Worksheet on 10 Times Table | Printable Multiplication Table | Video
Mar 21, 25 03:46 PM
Worksheet on 10 times table can be printed out. Homeschoolers can also use these multiplication table sheets to practice at home. -
5th Grade Prime and Composite Numbers | Definitions | Examples | Math
Mar 21, 25 12:18 AM
5th grade prime and composite numbers -
14 Times Table | Read and Write Multiplication Table of 14| Video
Mar 20, 25 04:03 PM
In 14 times table we will learn how to read and write multiplication table of 14. We read fourteen times table as:One time fourteen is 14 Two times fourteen are 28 Three times fourteen are 42 -
5th Grade Test of Divisibility Rules | Divisibility Rules From 2 to 12
Mar 20, 25 04:00 PM
In 5th grade test of divisibility rules we will learn about the exact divisibility of a number by the numbers from 2 to 12. The digit in the ones place should be 2, 4, 6, 8 or 0. -
5th Grade Even and Odd Numbers | Definitions | Examples
Mar 20, 25 02:45 AM
Numbers which are exactly divisible by 2 are even numbers. For example. 2,4,6,8,20,48,88, etc. are even numbers. They are multiples of 2. Numbers which are not exactly divisible by 2 are odd numbers…


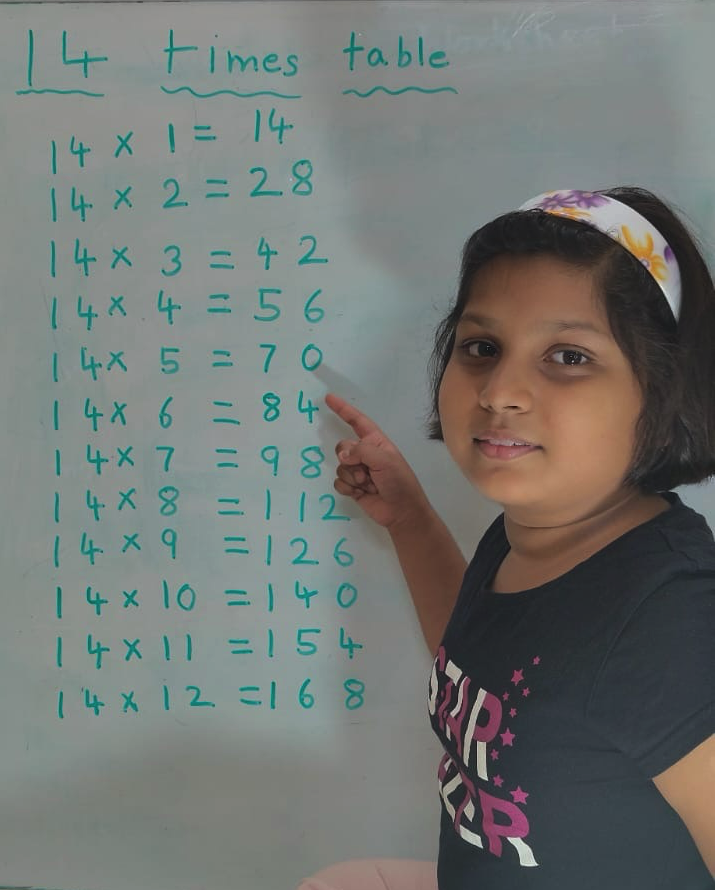
New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.