Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Problems on Representation of Rational Numbers on Number Line
Every number in mathematics can be represented on the number line. When we talk about rational number or fractions, they can also be represented on the number line. While representing rational numbers on number line one should always keep some important points in the mind such as:
(i) Every positive integer lies on the right side of zero on the number line and is greater than zero.
(ii) Every negative number is less than zero and lies on the left side of zero on the number line.
(iii) Every proper fraction has value between zero and one and lies between zero and one.
(iv) Since representation of improper fraction on number line is difficult, so first it is converted into the mixed fraction and is then represented on the number line.
1. Represent \(\frac{4}{5}\)on the number line.
Solution:
Since the given rational fraction is positive and is a proper fraction, so it’ll lie on the right side of zero on the number line and between 0 and 1. To represent this, we’ll divide the number line between 0 and 1 into 5 equal parts and the fourth part of the five parts will be \(\frac{4}{5}\)on the number line. This can be represented as:
2. Represent \(\frac{7}{3}\) on the number line.
Solution:
Take the number line with 0 at the point O. Take A\(_{1}\), A\(_{2}\), A\(_{3}\), ….. on the right of O at equal distances of 6 mm (6 is the multiple of the denominator 3).
A\(_{1}\), A\(_{2}\), A\(_{3}\), …. Represent the numbers 1, 2, 3, …. respectively.
1 is at a distance of 6 mm from O.
Therefore, \(\frac{7}{3}\) will be at a distance of \(\frac{7}{3}\) × 6 mm, i.e., 14 mm from O.
Now, take a point P on the right of A\(_{2}\) such that A\(_{2}\)P = 2 mm.
Clearly, Op = 14 mm.
Thus, P will represent the number \(\frac{7}{3}\) on the number line.
3. Place \(\frac{-3}{4}\) on the number line.
Solution:
The given rational fraction id negative and is a proper fraction. So, it will lie on the left of zero on the number line and will be between zero and negative one. To represent this on the number line first we need to divide number line between 0 and -1 into 4 equal parts and third part of the four parts will be required rational number on the number line. This can be represented as:
4. Represent \(\frac{8}{3}\) on the number line.
Solution:
Since the given rational fraction is a positive fraction and is an improper fraction. So, it’ll lie on the right side of zero on the number line. Now this is an improper fraction, so to represent this on the number line first we need to convert this into mixed fraction and then it will be represented on the number line. The mixed fraction conversion of the given fraction will be 2\(\frac{2}{3}\). Now this fraction will lie between 2 and 3 on the number line and number line between 2 and 3 will be divided into 3 equal parts and second part of the 3 parts will be the required fraction on the number line. This could be as:
5. Represent -\(\frac{7}{4}\) on the number line.
Solution:
The given rational fraction is a negative fraction and is an improper fraction. To represent it on the number line, first we need to convert the given fraction into mixed fraction. The mixed fraction of the given fraction is -1\(\frac{3}{4}\). So, the given fraction will lie on the on the left side of zero on the number line. It’ll lie between -1 and -2 on the number line. The number line between -1 and -2 will be divided into 4 equal parts and the third part of the four parts will be the required fraction on the number line. This can be represented as:
6. Represent the number -\(\frac{2}{5}\) on the number line.
Solution:
Take the number line with 0 at the point O. Take B\(_{1}\), B\(_{2}\), B\(_{3}\), ….. on the left of O at equal distances of 5 mm.
B\(_{1}\), B\(_{2}\), B\(_{3}\), …. represent the numbers -1, -2, -3, …. respectively.
-1 is at a distance of 5 mm from O.
Therefore, -\(\frac{2}{5}\) will be at a distance of \(\frac{2}{5}\) × 5 mm, i.e., 2 mm from O.
Now, take a point Q on the left of O such that OQ = 2 mm from O.
Thus, Q will represent the number -\(\frac{2}{5}\) on the number line.
Rational Numbers
Decimal Representation of Rational Numbers
Rational Numbers in Terminating and Non-Terminating Decimals
Recurring Decimals as Rational Numbers
Laws of Algebra for Rational Numbers
Comparison between Two Rational Numbers
Rational Numbers Between Two Unequal Rational Numbers
Representation of Rational Numbers on Number Line
Problems on Rational numbers as Decimal Numbers
Problems Based On Recurring Decimals as Rational Numbers
Problems on Comparison Between Rational Numbers
Problems on Representation of Rational Numbers on Number Line
Worksheet on Comparison between Rational Numbers
Worksheet on Representation of Rational Numbers on the Number Line
From Problems on Representation of Rational Numbers on Number Line to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
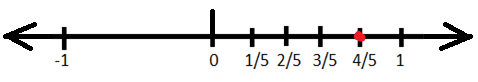
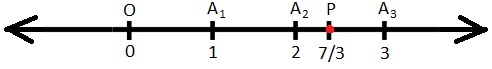
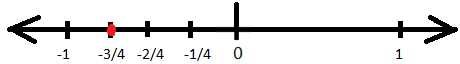
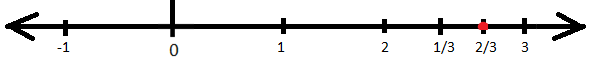



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.