Problems on Matrix Multiplication
Here we will solve different types of Problems on Matrix Multiplication.
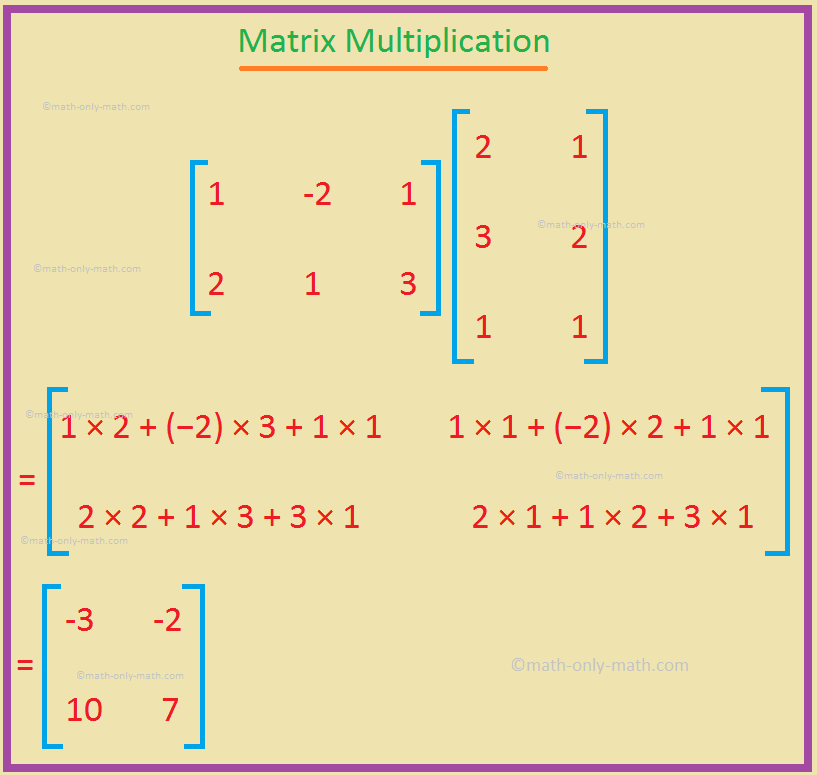
1. If A = [1−21213] and B = [213211], write down the matrix AB. Would it be possible to find the product of BA? If so, compute it, and if not, give reasons.
Solutions:
Here, matrix A is of the order 2 × 3 and matrix B is of the order 3 × 2.
So, the number of columns in A = the number of rows in B = 3.
So, AB can found.
AB = [1−21213][213211]
= [1×2+(−2)×3+1×11×1+(−2)×2+1×12×2+1×3+3×12×1+1×2+3×1]
= [−3−2107], which is a matrix of the order 2 × 2.
Now, the number of columns in B = the number of rows in A =
2. So, BA can be found, and the order of BA is 3 × 3.
BA = [213211][1−21213]
= [2×1+1×22×(−2)+1×12×1+1×33×1+2×23×(−2)+2×13×1+2×31×1+1×21×(−2)+1×11×1+1×3]
= [4−357−493−14]
Clearly, we can see that AB ≠ BA because they are not of the same order.
2. Let A = [2cos60∘−2sin∘−tan45∘cos0∘] and B = [cot45∘csc30∘sec60∘sin90∘]. Evaluate AB.
Solution:
AB = [2cos60∘−2sin∘−tan45∘cos0∘][cot45∘csc30∘sec60∘sin90∘]
= [2⋅12−2⋅12−11][−111−1]
= [1−1−11][1221]
= [1×1+(−1)×21×2+(−1)×1(−1)×1+1×2(−1)×2+1×1]
= [−111−1].
3. If A = [1221] and B = [2112], find A(BA).
Solution:
BA = [2112][1221]
= [2×1+1×22×2+1×11×1+2×21×2+2×1]
= [4554].
Therefore, A(BA) = [1221][4554]
= [1×4+2×51×5+2×42×4+1×52×5+1×4]
= [14131314]
From Problems on Matrix Multiplication to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Rules of Roman Numeration |Roman Number System|Roman Numeration System
Mar 18, 25 12:36 AM
We will learn about Roman Numeration and its rules. We know that there are seven basic Roman Numerals. They are I, V, X, L, C, D and M. These numerals stand for the number 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, 500 -
Divisible by 2 | Test of Divisibility by 2 |Rules of Divisibility by 2
Mar 17, 25 04:04 PM
A number is divisible by 2 if the digit at unit place is either 0 or multiple of 2. So a number is divisible by 2 if digit at its units place is 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8. -
Worksheet on 7 Times Table | Printable Multiplication Table | Video
Mar 17, 25 02:41 PM
Printable worksheet on 7 times table can be used from everywhere. Homeschoolers can also use these multiplication table sheets to practice at home. -
Worksheet on 6 Times Table | Printable Multiplication Table | Video
Mar 16, 25 03:09 PM
Printable worksheet on 6 times table can be used from everywhere. Homeschoolers can also use these multiplication table sheets to practice at home. -
Worksheet on 5 Times Table | Printable Multiplication Table | Video
Mar 16, 25 01:25 PM
Printable worksheet on 5 times table can be used from everywhere. Homeschoolers can also use these multiplication table sheets to practice at home.






New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.