Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Linear Pair of Angles
What is linear pair of angles?
Two angles form a linear pair if they have;
A common arm
A common vertex
Their interiors do not overlap
The sum of two angles is 180°.
Therefore, linear pair of angles are adjacent angles whose non-common arms are opposite rays.
Note:
All adjacent angles do not form a linear pair.
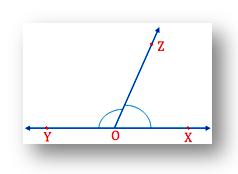
From the above figure we can observe; OX and OY are two opposite rays and ∠XOZ and ∠YOZ are the adjacent angles. Therefore, ∠XOZ and ∠YOZ form a linear pair.
If you measure ∠XOZ and ∠YOZ with the help of the protractor, you will find the sum of their measures equal to 180°.
Thus, the sum of the angles in a linear pair is 180°.
Worked-out problems on Linear Pair of angles:
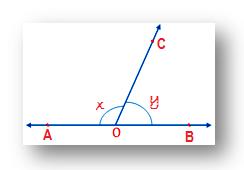
In the given figure, ∠AOC and ∠ BOC form a linear pair if x - y = 60°, find the value of x and y.
Solution:
Given x - y = 60° ………… (i)
We know that, x + y = 180° ………… (ii)
Adding (i) and (ii)
2x = 240°
x = 240°/2
Therefore, x = 120°
Since, x - y = 60°
or, 120° - y = 60°
or, 120° - 120° - y = 60° - 120°
or, -y = -60°
Therefore, y = 60°
● Lines and Angles
Fundamental Geometrical Concepts
Some Geometric Terms and Results
Complementary and Supplementary Angles
Parallel and Transversal Lines
7th Grade Math Problems
8th Grade Math Practice
From Linear Pair of Angles to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.


New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.