Hyperbola Formulae
Hyperbola formulae will help us to solve different types of problems on hyperbola in co-ordinate geometry.
1. x2a2 - y2b2 = 1, (a > b)
(i) The co-ordinates of the centre are (0, 0).
(ii) The co-ordinates of the vertices are (± a, 0) i.e., (-a, 0) and (a, 0).
(iii) The co-ordinates of the foci are (± ae, 0) i.e., (- ae, 0) and (ae, 0)
(iv) The length of transverse axis = 2a and the length of conjugate axis = 2b.
(v) The transverse axis is along x axis and the equations of transverse axes is y = 0.
(vi) The conjugate axis is along y axis and the equations of conjugate axes is x = 0.
(vii) The equations of the directrices are: x = ± ae i.e., x = - ae and x = ae.
(viii) The eccentricity of the hyperbola is b2 = a2(e2 - 1) or, e = √1+b2a2.
(ix) The length of the latus rectum 2 ∙ b2a = 2a(e2 - 1).
(x) The distance between the two foci = 2ae.
(xi) The distance between two directrices = 2 ∙ ae.
(xii) Focal distances of a point (x, y) are a ± ex
(xiii) The co-ordinates of the four ends of latera recta are (ae, b2a), (ae, -b2a), (- ae, b2a) and (- ae, -b2a).
(xiv) The equations of latera recta are x = ± ae i.e., x = ae and x = -ae.
2. x2b2 - y2a2 = 1, (a > b)
(i) The co-ordinates of the centre are (0, 0).
(ii) The co-ordinates of the vertices are (0, ± a) i.e., (0, -a) and (0, a).
(iii) The co-ordinates of the foci are (0, ± ae) i.e., (0, - ae) and (0, ae)
(iv) The length of transverse axis = 2a and the length of conjugate axis = 2b.
(v) The transverse axis is along Y-axis and the equations of conjugate axes is x = 0.
(vi) The transverse axis is along X-axis and the equations of conjugate axes is y = 0.
(vii) The equations of the directrices are: y = ± ae i.e., y = - ae and y = ae.
(viii) The eccentricity of the hyperbola is b2 = a2(e2 - 1) or, e = √1+b2a2
(ix) The length of the latus rectum 2 ∙ b2a = 2a (e2 - 1).
(x) The distance between the two foci = 2ae.
(xi) The distance between two directrices = 2 ∙ ae.
(xii) Focal distances of a point (x, y) are a ± ey
(xiii) The co-ordinates of the four ends of latera recta are (b2a, ae), (-b2a, ae), (b2a, -ae) and (-b2a, -ae).
(xiv) The equations of latera recta are y = ± ae i.e., y = ae and y = -ae.
3. (x−α)2a2 - (y−β)2b2 = 1, (a > b)
(i) The co-ordinates of the centre are (α, β).
(ii) The co-ordinates of the vertices are (α ± a, β) i.e., (α - a, β) and (α + a, β).
(iii) The co-ordinates of the foci are (α ± ae, β) i.e., (α - ae, β) and (α + ae, β)
(iv) The length of transverse axis = 2a and the length of conjugate axis = 2b.
(v) The transverse axis is along parallel to x axis and the equations of transverse axes is y = β.
(vi) The conjugate axis is along parallel to y axis and the equations of conjugate axes is x = α.
(vii) The equations of the directrices are: x = α ± ae i.e., x = α - ae and x = α + ae.
(viii) The eccentricity of the hyperbola is b2 = a2(e2 - 1) or, e = √1+b2a2
(ix) The length of the latus rectum 2 ∙ b2a = 2a (e2 - 1).
(x) The distance between the two foci = 2ae.
(xi) The distance between two directrices = 2 ∙ ae.
4. (x−α)2b2 - (y−β)2a2 = 1, (a > b)
(i) The co-ordinates of the centre are (α, β).
(ii) The co-ordinates of the vertices are (α, β ± a) i.e., (α, β - a) and (α, β + a).
(iii) The co-ordinates of the foci are (α, β ± ae) i.e., (α, β - ae) and (α, β + ae).
(iv) The length of transverse axis = 2a and the length of conjugate axis = 2b.
(v) The transverse axis is along parallel to Y-axis and the equations of transverse axes is x = α.
(vi) The conjugate axis is along parallel to X-axis and the equations of conjugate axes is y = β.
(vii) The equations of the directrices are: y = β ± ae i.e., y = β - ae and y = β + ae.
(viii) The eccentricity of the hyperbola is b2 = a2(e2 - 1) or, e = √1+b2a2
(ix) The length of the latus rectum 2 ∙ b2a = 2a (e2 - 1).
(x) The distance between the two foci = 2ae.
(xi) The distance between two directrices = 2 ∙ ae.
5. The point P (x1, y1) lies outside, on or inside the hyperbola x2a2 - y2b2 = 1 according as x21a2 - y21b2 – 1 < 0, = or > 0.
6. If x2a2 - y2b2 = 1 is an hyperbola, then its auxiliary circle is x2 + y2 = a2.
7. The equations x = a sec θ, y = b tan θ taken together are called the parametric equations of the hyperbola x2a2 - y2b2 = 1
8. The co-ordinates of the point having eccentric angle θ can be written as (a sec θ, b tan θ). Here (a sec θ, b tan θ) are known as the parametric co-ordinates of the point P.
9. The equation of rectangular hyperbola is x2 - y2 = a2.
Some of the properties of rectangular hyperbola:
(i) The transverse axis is along x-axis
(ii) The conjugate axis is along y-axis
(iii) The length of transverse axis = 2a
(iv) The length of conjugate axis = 2a
(v) The eccentricity of the rectangular hyperbola = √2.
10. The conjugate hyperbola of the hyperbola x2a2 - y2b2 = 1 is - x2a2 + y2b2 = 1
In other wards two hyperbolas x2a2 -
y2b2 = 1 …………………(i) and - x2a2 +
y2b2 = 1 ……………….(ii) are conjugate to one another, if e1 and e2 he the eccentricities of (i) and (ii) respectively, then b2 = a2(e12 - 1) and a2 = b2(e22 - 1).
● The Hyperbola
- Definition of Hyperbola
- Standard Equation of an Hyperbola
- Vertex of the Hyperbola
- Centre of the Hyperbola
- Transverse and Conjugate Axis of the Hyperbola
- Two Foci and Two Directrices of the Hyperbola
- Latus Rectum of the Hyperbola
- Position of a Point with Respect to the Hyperbola
- Conjugate Hyperbola
- Rectangular Hyperbola
- Parametric Equation of the Hyperbola
- Hyperbola Formulae
- Problems on Hyperbola
From Hyperbola Formulae to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
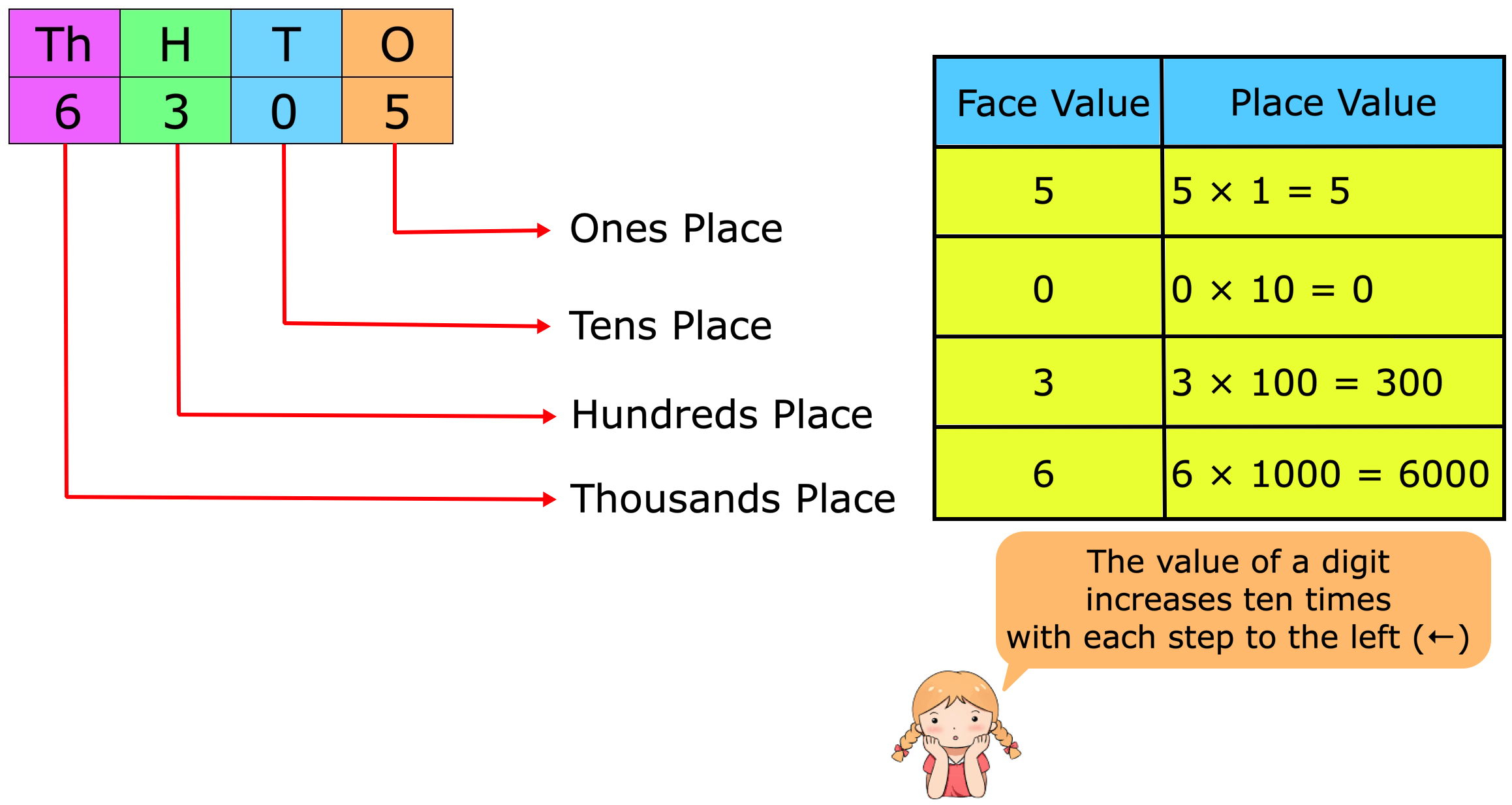
Place Value and Face Value | Place and Face Value of Larger Number
Apr 13, 25 03:12 PM
The place value of a digit in a number is the value it holds to be at the place in the number. We know about the place value and face value of a digit and we will learn about it in details. We know th… -
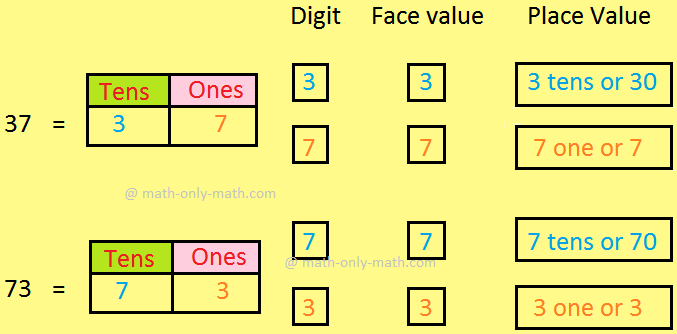
Face Value and Place Value|Difference Between Place Value & Face Value
Apr 13, 25 03:07 PM
What is the difference between face value and place value of digits? Before we proceed to face value and place value let us recall the expanded form of a number. The face value of a digit is the digit… -
Place Value and Face Value | Basic Concept on Place Value | Face Value
Apr 13, 25 02:59 PM
Learn the easiest way to understand the basic concept on place value and face value in the second grade. Suppose we write a number in figures 435 in words we write four hundred thirty five. -
Expressing Place Value and Face Value | International & Indian System
Apr 13, 25 02:35 PM
We will learn expressing place value and face value of a digit in any number in International and Indian system. Place value: We know how to find out the place value of a digit in any number. -
5th Grade Decimals | Word Problem on Decimals | Concept of Decimals
Apr 13, 25 02:16 PM
A fractional number whose denominator is 10 or multiple of 10 is called a decimal. Every decimal has two parts whole number part and decimal part. These two parts are separated by a dot or point. This…



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.