Hexa-decimal Number System
The hexa-decimal number system has a radix or base 16. It requires 16 symbols to represent a number in this system. The symbols are 0 to 9, A, B, C, D, E, F where the symbols A, B, C, D, E, F represent the decimal numbers 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 respectively. Let us recall the conversion table for the decimal numbers 0 to 15 and their binary, octal and hexa-decimal equivalents.
The conversion of hexa-decimal numbers to their decimal equivalents is straight-forward and follows the same rules as that of octal or binary to decimal. Similarly, conversion of decimal to hexa-decimal may be worked out with the help of division or multiplication, as the case may be, by the radix 16.
The example on hexa-decimal number system will help us to understand the procedure:
1. Convert B6A16 to its decimal equivalent.Solution:
B6A16
= 11 × 162 + 6 × 161 + 10 × 160
= 2816 + 96 + 10
= 292210
Therefore, B6A16 = 292210
2. Convert 391710 to its hexa-decimal equivalent
Solution:
391710
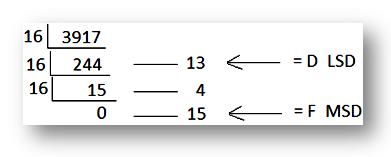
Therefore, 391710 = F4D16
- Why Binary Numbers are Used
- Binary to Decimal Conversion
- Conversion of Numbers
- Hexa-decimal Number System
- Conversion of Binary Numbers to Octal or Hexa-decimal Numbers
- Octal and Hexa-Decimal Numbers
- Signed-magnitude Representation
- Radix Complement
- Diminished Radix Complement
- Arithmetic Operations of Binary Numbers
From Hexa-decimal Number System to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Place Value and Face Value | Place and Face Value of Larger Number
Apr 13, 25 03:12 PM
The place value of a digit in a number is the value it holds to be at the place in the number. We know about the place value and face value of a digit and we will learn about it in details. We know th… -
Face Value and Place Value|Difference Between Place Value & Face Value
Apr 13, 25 03:07 PM
What is the difference between face value and place value of digits? Before we proceed to face value and place value let us recall the expanded form of a number. The face value of a digit is the digit… -
Place Value and Face Value | Basic Concept on Place Value | Face Value
Apr 13, 25 02:59 PM
Learn the easiest way to understand the basic concept on place value and face value in the second grade. Suppose we write a number in figures 435 in words we write four hundred thirty five. -
Expressing Place Value and Face Value | International & Indian System
Apr 13, 25 02:35 PM
We will learn expressing place value and face value of a digit in any number in International and Indian system. Place value: We know how to find out the place value of a digit in any number. -
5th Grade Decimals | Word Problem on Decimals | Concept of Decimals
Apr 13, 25 02:16 PM
A fractional number whose denominator is 10 or multiple of 10 is called a decimal. Every decimal has two parts whole number part and decimal part. These two parts are separated by a dot or point. This…



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.