Graph of y = sin x
y = sin x is periodic function. The period of y = sin x is 2π. Therefore, we will draw the graph of y = sin x in the interval [-π, 2π].
For this, we need to take the different values of x at intervals of 10°. Then by using the table of natural sines we will get the corresponding values of sin x. Take the values of sin x correct to two place of decimal. The values of sin x for the different values of x in the interval [-π, 2π] are given in the following table.
We draw two mutually perpendicular straight lines XOX’ and YOY’. XOX’ is called the x-axis which is a horizontal line. YOY’ is called the y-axis which is a vertical line. Point O is called the origin.
Now represent angle (x) along x-axis and y (or sin x) along y-axis.
Along the x-axis: Take 1 small square = 10°.
Along the y-axis: Take 10 small squares = 1 unity.
Now plot the above tabulated values of x and y on the co-ordinate graph paper. Then join the points by free hand. The continuous curve obtained by free hand joining is the required graph of y = sin x.
Steps to draw the graph of y = c
sin ax.
Steps I: Obtain the values of a and c.
Step II: Draw the graph of y = sin x and mark the points where y = sin x crosses x-axis.
Step III: Divide the x-coordinate of the points where y = sin x crosses x-axis by a and mark maximum and minimum values of y = c sin ax as c and –c on y-axis.
The graph obtained is the required graph of y = c sin ax.
Properties of y = sin x:
(i) The graph of the function y = sin x is continuous and extends on either side in symmetrical wave form.
(ii) Since the graph intersects the x-axis at the origin and at points where x is an even multiple of 90°, hence sin x is zero at x = nπ where n = 0, ±1, ±2, ±3, ±4, ……………... .
(iii) The ordinate of any point on the graph always lies between 1 and - 1 i.e., - 1 ≤ y ≤ 1 or ,-1 ≤ sin x ≤ 1 hence, the maximum value of sin x is 1 and its minimum value is - 1 and these values occur alternately at π2, 3π2, 5π2,……… i. e., at x = (2n + 1)π2, where n = 0, ±1, ±2, ±3, ±4, ……………...
(iv) Since the function y= sin x is periodic of period 2π, hence the portion of the graph between 0 to 2π is repeated over and over again on either side.
Solved example to sketch the graph of y = sin x:
Sketch the graph of y = 2 sin 3x.
Solution:
To obtain the graph of y = 2 sin 3x we first draw the graph y = sin x in the interval [0, 2n] and then divide the x-coordinates of the points where it crosses x-axis by 3. The maximum and minimum values are 2 and -2 respectively.
● Graphs of Trigonometrical Functions
- Graph of y = sin x
- Graph of y = cos x
- Graph of y = tan x
- Graph of y = csc x
- Graph of y = sec x
- Graph of y = cot x
From Graph of y = sin x to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Adding 1-Digit Number | Understand the Concept one Digit Number |Video
Mar 07, 25 03:55 PM
Understand the concept of adding 1-digit number with the help of objects as well as numbers. -
Vertical Addition | How to Add 1-Digit Number Vertically? | Problems
Mar 07, 25 02:35 PM
Now we will learn simple Vertical Addition of 1-digit number by arranging them one number under the other number. How to add 1-digit number vertically? -
13 Times Table | Read and Write Multiplication Table of 13|Times Table
Mar 07, 25 02:33 PM
In 13 times table we will learn how to read and write multiplication table of 13. We read thirteen times table as: One time thirteen is 13 Two times thirteen are 26 Three times thirteen are 39 -
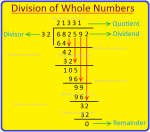
Division of Whole Numbers |Relation between Dividend, Divisor Quotient
Mar 05, 25 03:36 PM
Relation between Dividend, Divisor, Quotient and Remainder is. Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder. To understand the relation between dividend, divisor, quotient and remainder let us follow the… -
Multiplication of Whole Numbers | Whole Numbers|Multiplication|Numbers
Mar 05, 25 03:29 PM
Multiplication of whole numbers is the sort way to do repeated addition. The number by which any number is multiplied is known as the multiplicand. The result of the multiplication is known as the pro…

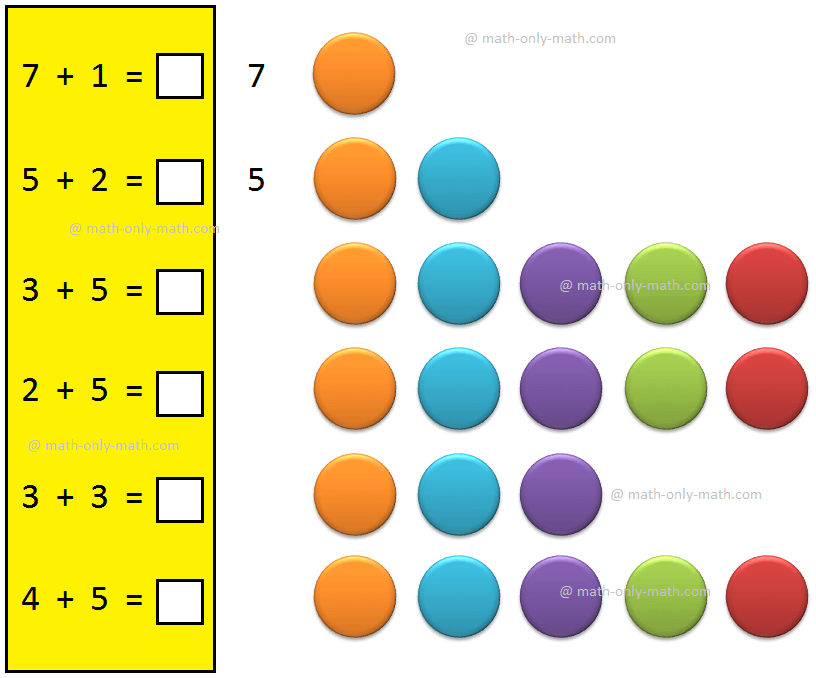



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.