Construction of Perpendicular Bisector
Here we will learn how to construct a perpendicular bisector of a line segment.
The perpendicular bisector of a line segment is the line that is perpendicular to the line segment at its mid-point.
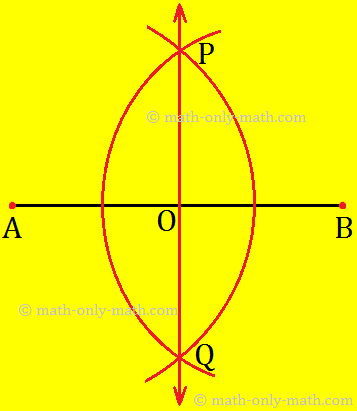
In the adjoining Fig., ↔PO is the perpendicular bisector of ¯AB bisecting ¯AB at O i.e., ¯AO = ¯BO
First Method: To Draw the Perpendicular Bisector with the Help of Transparent Tapes
Working Rules To Draw the Perpendicular Bisector:
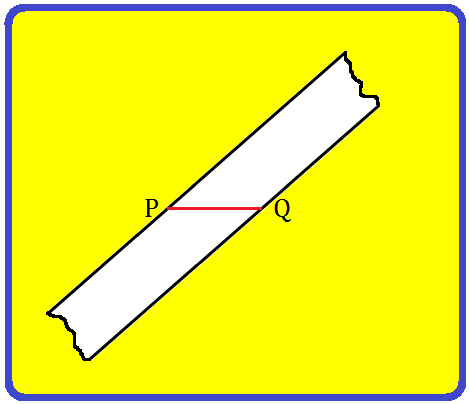
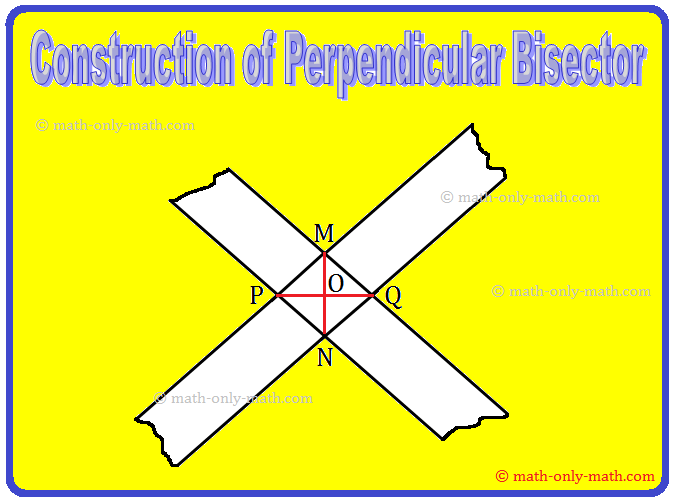
Step I: Draw a line segment PQ.
Step II: Paste a strip of a transparent rectangular taps diagonally across the end-points P and Q as shown in the figure.
Step III: Repeat the process as in step-2 by placing another taps over P and Q just diagonally across the previous one. Thus, two strips cross at M and N.
Step IV: Join M and N to get ¯MN and ¯PQ as the required perpendicular bisectors of each other.
Second Method: To Draw the Perpendicular Bisector using Ruler and Compasses
Working Rules To Draw the Perpendicular Bisector:
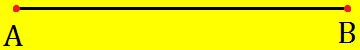
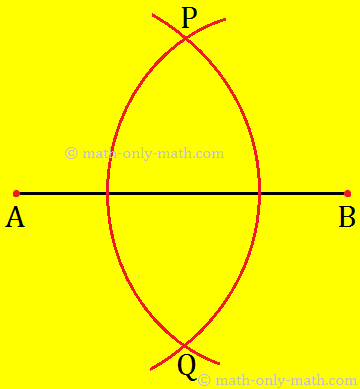
Step I: Draw a line segment AB of any length.
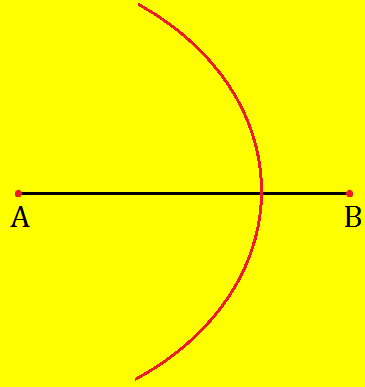
Step II: Using compass, draw an arc with A as centre and a radius more than half the length of ¯AB
Step III: With B as a centre and same radius as in step-II, draw another arc to intersect the previous arc at P and Q.
Step III: Join P and Q to get ↔PQ. It cuts AB at O. This line PQ bisects the given line segment AB at O. i.e. ¯AO = ¯BO
What would happen?
In steps II and III above, what would happen, if we take less than half of the length as radius and draw arcs?
Solved Examples on Construction of Perpendicular Bisector:
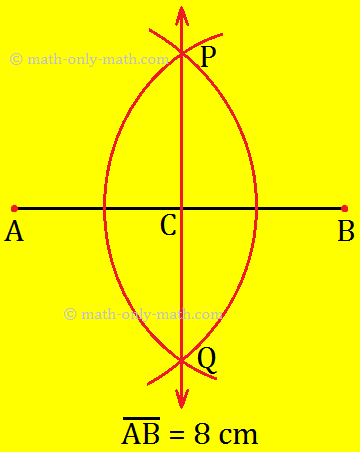
1. Draw a line segment AB of length 8 cm. Using compass, divide it into four equal parts.
Solution:
Step I: Draw a line segment AB = 8 cm and draw a perpendicular bisector using steps given in the Working Rules.
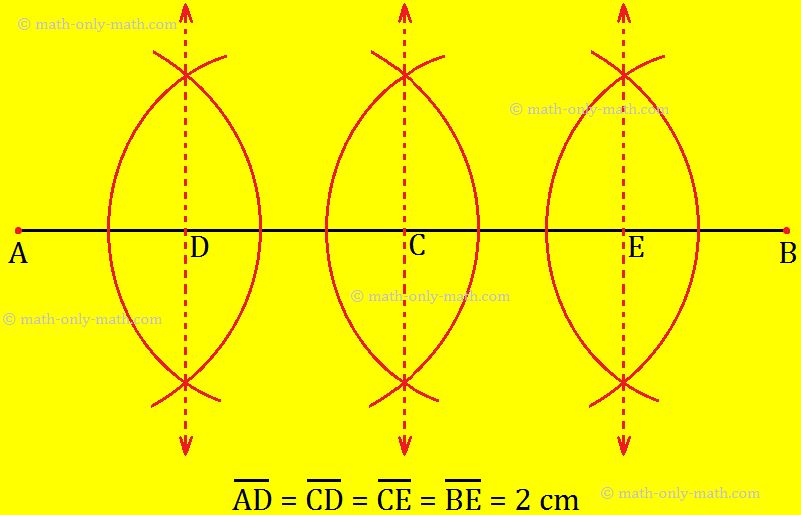
Step II: In step I, we have divided ¯AB into two equal parts ¯AC and ¯BC Similarly, draw the perpendicular bisectors of ¯AC and overline BC separately.
Now, we obtain four equal parts of ¯AB
i.e., ¯AD = ¯CD = ¯CE = ¯BE = 2 cm .
Worksheet on Construction of Perpendicular Bisector:
1. Draw a line segment of 8.5 cm and draw its perpendicular bisector.
2. Divide a line segment of length 8 cm into four equal parts using compass.
3. Draw a circle of radius 5 cm. Draw two chords on it. Constrct the perpendicular bisector of these chords. Where do they meet?
4. Draw a triangle. Construct three perpendicular bisectors on each of its side. Check whether all three bisectors meet at one point.
5. Divide a line segment of length 10 cm into four equal parts using compass.
From CConstruction of Perpendicular Bisector of a Line Segment to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Counting Numbers from 1 to 50 | Match the Number | Missing Numbers
Apr 04, 25 03:46 PM
In counting numbers from 1 to 50, recognize the numbers, count and then join the numbers in the correct number order. Here we mainly need eye-hand coordination to draw the picture and maintain the num -
Counting Eleven to Twenty with Numbers and Words |Numbers from 11 - 20
Apr 04, 25 03:21 PM
Counting eleven to twenty with numbers and words are explained below. One ten and one more is eleven. Eleven comes after ten. One ten and two more is twelve. Twelve comes after eleven. -
5th Grade BODMAS Rule Worksheet | PEMDAS | Order of operations|Answers
Apr 03, 25 03:11 PM
In 5th Grade BODMAS Rule Worksheet you will get different types of problems on mathematical expressions involving different operations, mathematical expression with 'brackets' and 'of' and simplifying… -
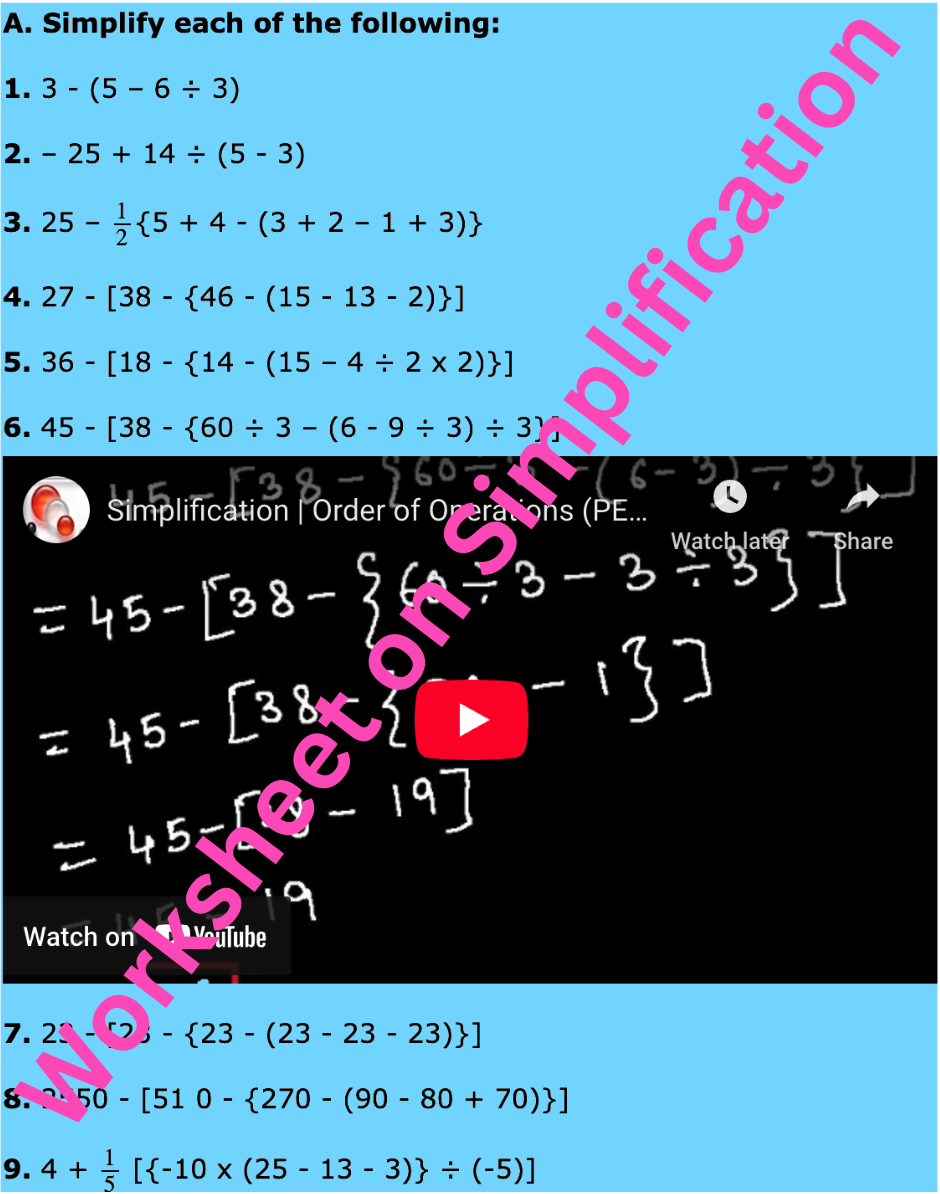
Worksheet on Simplification | Simplify Expressions | BODMAS Questions
Apr 03, 25 02:58 PM
In worksheet on simplification, the questions are based in order to simplify expressions involving more than one bracket by using the steps of removal of brackets. This exercise sheet -
Divisible by 2 Video |Test of Divisibility by 2 Trick| Rules| Examples
Apr 03, 25 10:25 AM
A number is divisible by 2 if the digit at unit place is either 0 or multiple of 2. So a number is divisible by 2 if digit at its units place is 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8.




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.