Basic Proportionality Theorem
Here we will learn how to prove the basic proportionality theorem with diagram.
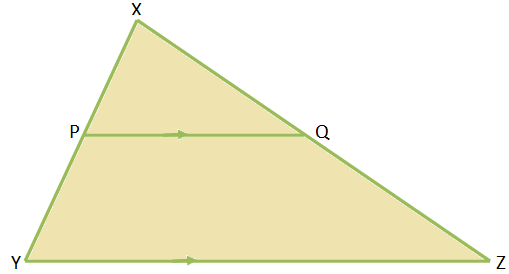
A line drawn parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two sides proportionally.
Given: In ∆XYZ, P and Q are points on XY and XZ respectively, such that PQ ∥ YZ.
To prove: XPPY = XQQZ.
Proof:
|
Statement |
Reason |
|
1. In ∆XYZ and ∆XPQ, (i) ∠YXZ = ∠PXQ (ii) ∠XYZ = ∠XPQ |
1. (i) Common angle (ii) Corresponding angles |
|
2. ∆XYZ ∼ ∆XPQ |
2. AA criterion of similarity. |
|
3. XYXP = XZXQ |
3. Corresponding sides of similar triangles are proportional. |
|
4. XYXP – 1 = XZXQ – 1 ⟹ XY−XPXP = XZ−XQXQ ⟹ PYXP = QZXQ |
4. By subtracting 1 from both sides of statement 3. |
|
5. XPPY = XQQZ |
5. Taking reciprocals of both sides in statement 4. |
Solved examples using basic proportionality theorem:
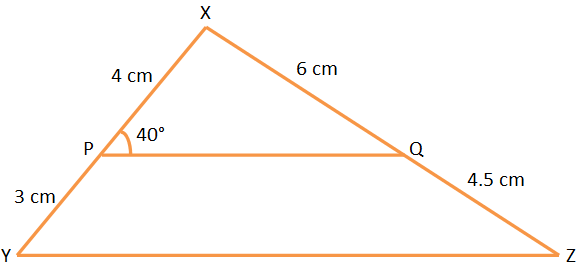
1. If in a ∆XYZ, P and Q are two points on XY and XZ respectively such that XP = 4 cm, PY = 3 cm, XQ = = 6 cm, QZ = 4.5 cm and ∠XPQ = 40° then find ∠XYZ.
Solution:
Here, XPPY = 4cm3cm = 43, and
XQQZ = 6cm4.5cm = 43
Therefore, XPPY = XQQZ
⟹ PQ ∥ YZ
Therefore, ∠XYZ = ∠XPQ = 40°.
2. In the given figure, if XP = 6 cm, YP = 2 cm, XQ = 7.5 cm, find QZ.
Solution:
By basic proportionality theorem,
XPPY = XQQZ
⟹ 6cm2cm = 7.5cmQZ
⟹ QZ = 7.5cm×26
⟹ QZ = 2.5 cm.
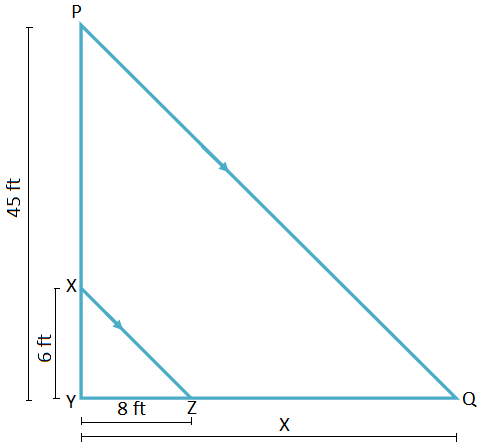
3. At a certain time of the day, a man, 6 feet tall, casts his shadow 8 feet long. Find the length of the shadow cast by a building 45 feet high, at the same time.
Solution:
Let the length of the shadow of the building be x.
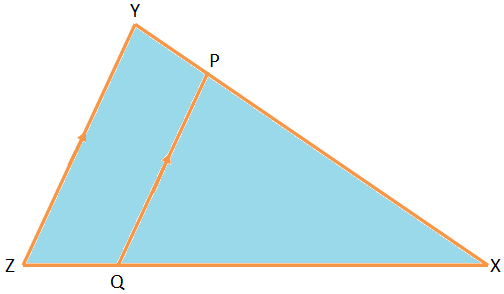
As the source of light is the sun, XZ ∥ PQ and, hence ∆YXZ ∼ ∆YPQ.
Therefore, Height of the ManHeight of the Building = Length of Shadow Cast by the ManLength of Shadow Cast by the Building
⟹ 6ft45ft = 8ftx
⟹ x = 60 feet.
From Basic Proportionality Theorem to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Counting Numbers from 1 to 50 | Match the Number | Missing Numbers
Apr 04, 25 03:46 PM
In counting numbers from 1 to 50, recognize the numbers, count and then join the numbers in the correct number order. Here we mainly need eye-hand coordination to draw the picture and maintain the num -
Counting Eleven to Twenty with Numbers and Words |Numbers from 11 - 20
Apr 04, 25 03:21 PM
Counting eleven to twenty with numbers and words are explained below. One ten and one more is eleven. Eleven comes after ten. One ten and two more is twelve. Twelve comes after eleven. -
5th Grade BODMAS Rule Worksheet | PEMDAS | Order of operations|Answers
Apr 03, 25 03:11 PM
In 5th Grade BODMAS Rule Worksheet you will get different types of problems on mathematical expressions involving different operations, mathematical expression with 'brackets' and 'of' and simplifying… -
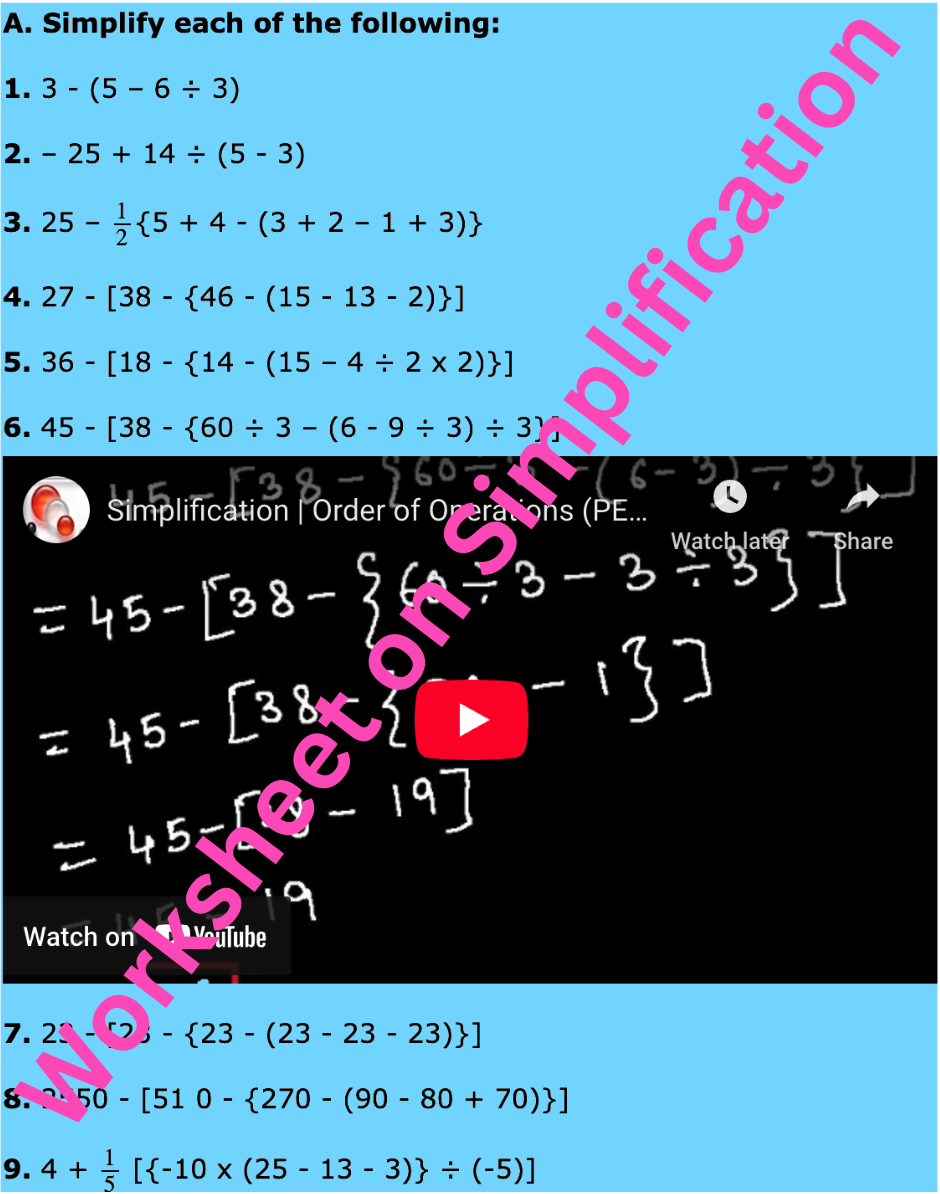
Worksheet on Simplification | Simplify Expressions | BODMAS Questions
Apr 03, 25 02:58 PM
In worksheet on simplification, the questions are based in order to simplify expressions involving more than one bracket by using the steps of removal of brackets. This exercise sheet -
Divisible by 2 Video |Test of Divisibility by 2 Trick| Rules| Examples
Apr 03, 25 10:25 AM
A number is divisible by 2 if the digit at unit place is either 0 or multiple of 2. So a number is divisible by 2 if digit at its units place is 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8.




New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.