Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Divide on a Number Line
How to divide on a number line?
Learn to divide using number line to find the quotient.
We can do repeated subtraction on the number line to find division.
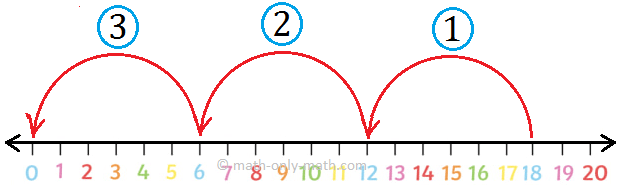
1. Let us find 15 ÷ 5.
Thus, 15 ÷ 5 = 3
Division on the Number Line:
For dividing on the number line, we do backward skip counting.
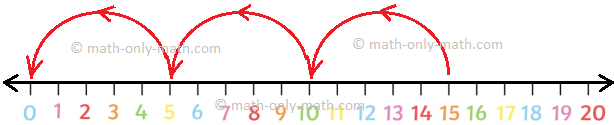
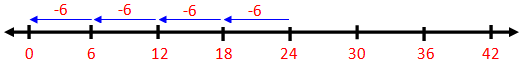
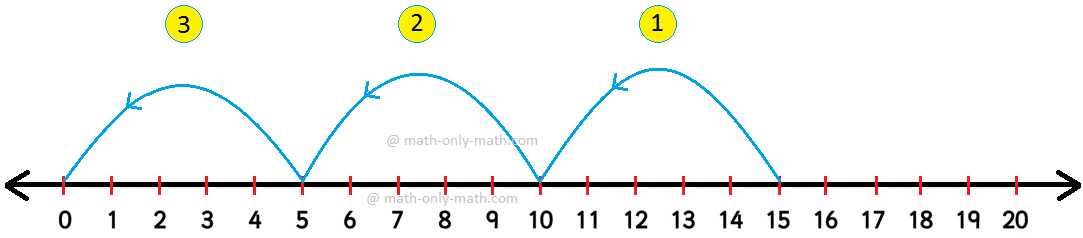
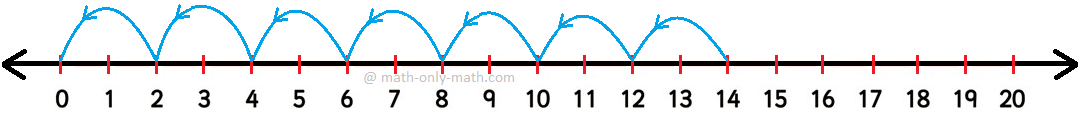
2. Let us divide 18 by 6 on the number line.
To divide 18 by 6 on the number line, we start from 18 and skip count backwards in 6s till we reach 0.
The number of jumps is 3.
Therefore, 18 ÷ 6 = 3.
Solved Examples to show Divide on a
Number Line:
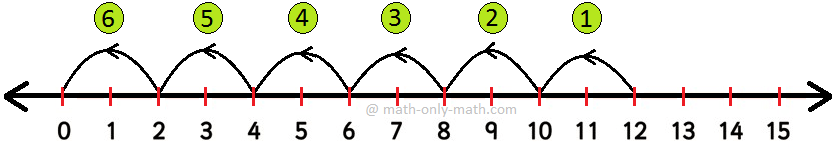
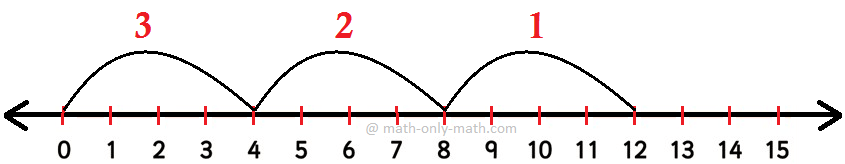
1. Solve 14 ÷ 7
Solution:
7 is subtracted repeatedly from 14 using the number line
When 7 is subtracted 2 times from 14 in the number line, then we get the remainder zero.
Thus, 7 is subtracted from 14, 2 times.
Hence, 14 ÷ 7 = 2, 2 is the quotient.
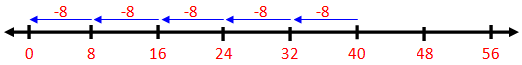
2. Divide 40 ÷ 8
Using the number line 8 is subtracted repeatedly from 40
When 8 is subtracted 5 times from 40 in the number line, then we get the remainder zero.
Thus, 8 is subtracted from 40, 5 times.
Hence, 40 ÷ 8 = 5, 5 is the quotient.
3. Solve 24 by 6
Solution:
6 is subtracted repeatedly from 24 using the number line
When 6 is subtracted 4 times from 24 in the number line, then we get the remainder zero.
Thus, 6 can be subtracted from 24, 4 times.
Hence, 24 ÷ 6 = 4, 4 is the quotient.
4. Divide 15 ÷ 3
3 is subtracted repeatedly from 15 using the number line
3 is subtracted from 15, five times in the number line, then we get the remainder zero.
Thus, 3 can be subtracted from 15 five times.
Hence, 15 ÷ 3 = 5, 5 is the quotient.
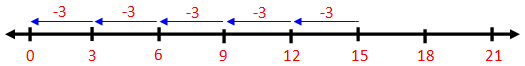
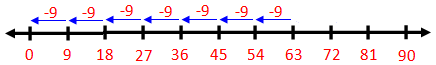
5. Divide 63 ÷ 9
9 is subtracted repeatedly from 63 using the number line
9 is subtracted from 63, seven times in the number line, then we get the remainder zero.
Thus, 9 can be subtracted from 63 seven times.
Hence, 63 ÷ 9 = 7, 7 is the quotient.
On the number line, we can show repeated subtraction by counting backward in equal jumps.
6. Divide 12 by 2.
Start from 12. Jump backwards by taking jumps of 2 steps each. Stop at 0.
Note that 6 jumps are needed to reach 0.
12 - 2 = 10; 10 - 2 = 8; 8 - 2 = 6; 6 - 2 = 4; 4 - 2 = 2; 2 - 2 = 0
We write: 12 ÷ 2 = 6
We read: 12 divided by 2 equals 6.
7. Divide 15 by 5.
Start from 15. Jump backwards by taking jumps of 5 steps each. Stop at 0.
Note that 3 jumps are needed to reach 0.
15 - 5 = 10; 10 - 5 = 5; 5 - 5 = 0
We write: 15 ÷ 5 =3
We read: 15 divided by 5 equals 3.
Division on a Number Line
8. Divide 12 by 4 using number line.
Number line can be used for division. Let us divide 12 by 4 using the number line.
To divide 12 by 4, place your finger on the number 12. Now, take jumps of 4 each to reach 0. The number of jumps is 3. So, 12 ÷ 4 = 3.
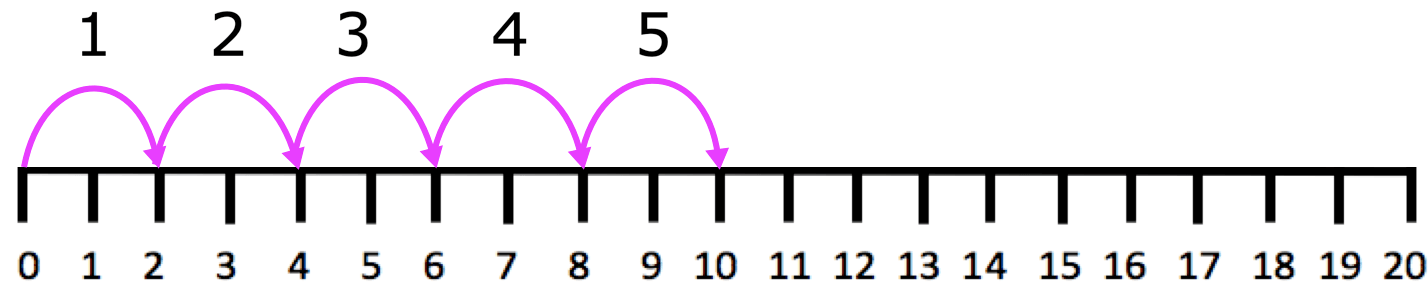
9. 10 ÷ 2 using the number line.
Take jumps of 2 starting from 0 till you reach 10.
How many jumps have you taken?
You have taken 5 jumps.
Therefore, 10 ÷ 2 = 5.
Division of Whole Numbers on Number Line
Using the number line, write the whole number which is quotient of 14 ÷ 7. Since division is repeated subtraction, therefore, to evaluate 14 ÷ 7, first start from 14 and move 7 units at a time to the left till 0 is reached, as shown in the following figure.
Hence, 14 ÷ 7 = number of moves = 2.
The above examples will help us to solve various division problems on 1-digit number and 2-digit number by a single digit number using number line.
Worksheet on Divide on a Number Line:
Questions and Answers on Division on a Number Line:
1. Use the number line to find the division by repeated subtraction.
(i) Find 12 ÷ 2
12 ÷ 2 = _____
(ii) Find 18 ÷ 3
18 ÷ 3 = _____
(iii) Find 20 ÷ 4
20 ÷ 4 = _____
Answer:
(i) 12 ÷ 2 = 6
(ii) 18 ÷ 3 = 6
(iii) 20 ÷ 4 = 5
2. Divide 6 by 3.
So, 6 ÷ 3 = _____
Answer:
2. 2
3. Divide on the number line. One has been done for you.
(i)
14 ÷ 2 = 7
(ii)
12 ÷ 4 = _____
(iii)
18 ÷ 3 = _____
(iv)
16 ÷ 4 = _____
(v)
20 ÷ 4 = _____
(vi)
10 ÷ 5 = _____
(vii)
12 ÷ 3 = _____
Answer:
3. (ii) 3
(iii) 6
(iv) 4
(v) 5
(vi) 2
(vii) 4
4. Write the division fact and the repeated subtraction for each of the following. Also show the division on the number line.
(i) 16 packets of biscuits shared equally among 8 children
Division fact: _____ ÷ _____ = _____
Repeated subtraction: ____________________
Division on the number line:
(ii) 18 toffees distributed equally among 6 boys
Division fact: _____ ÷ _____ = _____
Repeated subtraction: ____________________
Division on the number line:
(iv) 20 toys distributed equally among 4 girls
Division fact: _____ ÷ _____ = _____
Repeated subtraction: ____________________
Division on the number line:
Answer:
4. (i) Division fact: 16 ÷ 8 = 2
Repeated subtraction: 16 - 8 - 8 = 0
(ii) Division fact: 18 ÷ 6 = 3
Repeated subtraction: 18 - 6 - 6 - 6 = 0
(iii) Division fact: 20 ÷ 4 = 5
Repeated subtraction: 20 - 4 - 4 - 4 - 4 - 4 = 0
From Divide on a Number Line to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
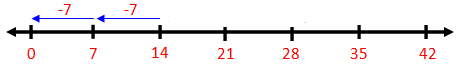
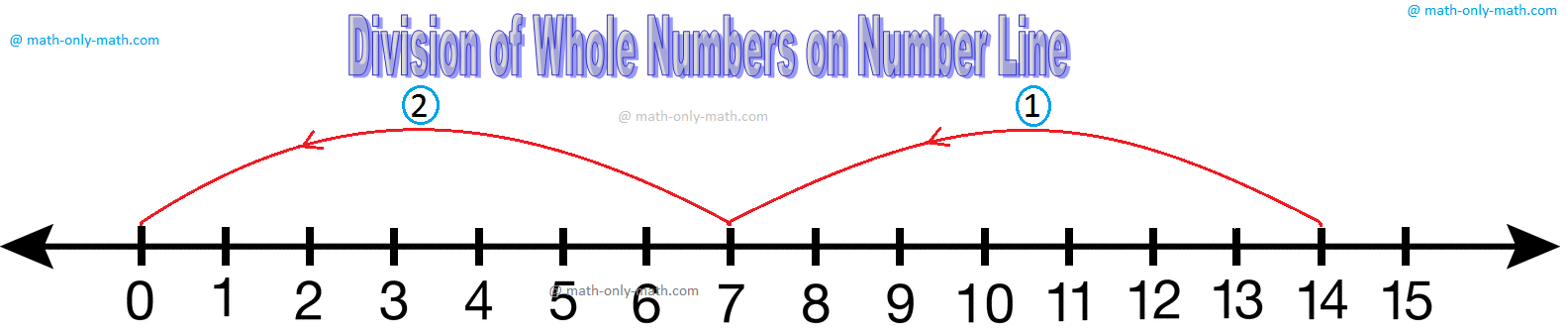



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.