Binary Number System
Here we will discuss about the binary number system we already know binary numbers play a vital role in the design of digital computers.
Hence a detailed discussion of binary number system is given in this section. Binary number system uses two symbols 0 and 1 and its radix is 2. The symbols 0 and 1 are generally called BITS which is a contraction of the two words Binary digits.
An n-bit binary number of the form an-1 an-2 ….. a1 a0 where each ai (i = 0, 1, …. n - 1) is either 0 or 1 has the magnitude.an-1 2n-1 + an-2 2n-2 + …….+ a1 21 + a020.
For fractional binary numbers, the base has negative integral powers starting with -1 for the bit position just after the binary point.
The bit at the extreme left of a binary number has the highest positional value and is usually called the Most Significant Bit or MSB. Similarly, the bit occupying the extreme right position of a given binary number has the least positional value and is referred to as the Least Significant Bit or LSB.
To facilitate the distinction between different number
systems, we generally use the respective radix as a subscript of the number.
However the subscript will not be used when there is no scope of confusion.
In binary number system a few examples on binary numbers and their decimal equivalents are given below:
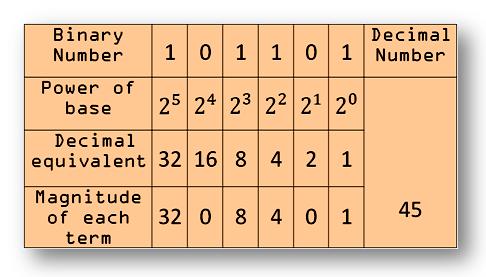
1011012 = 1 × 25 + 0 × 24 + 1 × 23 + 1 × 22 + 0 × 21 + 1 × 20= 32 + 0 + 8 + 4 + 0 + 1
= 4510
The above results can be more clearly expressed in the following manner:
Binary point
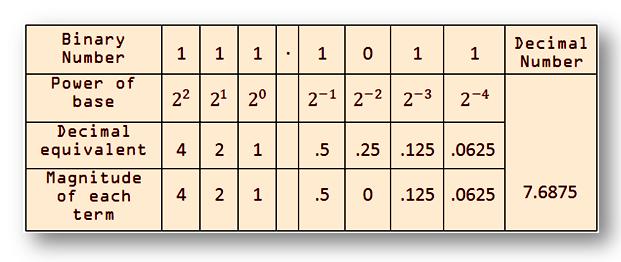
= 1 × 22 + 1 × 21 + 1 × 20 + 1 × 2-1 + 0 × 2-2 + 1 × 2-3 + 1 × 2-4
= 4 + 2 + 1 + .5 + 0 + .125 + .0625
= 7.687510
The above results can be more clearly expressed in the following manner:
These are the basic examples shown above.
- Why Binary Numbers are Used
- Binary to Decimal Conversion
- Conversion of Numbers
- Hexa-decimal Number System
- Conversion of Binary Numbers to Octal or Hexa-decimal Numbers
- Octal and Hexa-Decimal Numbers
- Signed-magnitude Representation
- Radix Complement
- Diminished Radix Complement
- Arithmetic Operations of Binary Numbers
From Binary Number System to Home Page
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math. Use this Google Search to find what you need.
Recent Articles
-
Fundamental Operations on Large Numbers Worksheet | 5th Grade Numbers
Mar 16, 25 11:37 AM
fundamental operations on large numbers worksheet -
Word Problems on Division | Examples on Word Problems on Division
Mar 13, 25 01:01 PM
Word problems on division for fourth grade students are solved here step by step. Consider the following examples on word problems involving division: 1. $5,876 are distributed equally among 26 men. H… -
Division of Whole Numbers |Relation between Dividend, Divisor Quotient
Mar 13, 25 12:41 PM
Relation between Dividend, Divisor, Quotient and Remainder is. Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder. To understand the relation between dividend, divisor, quotient and remainder let us follow the… -
Adding 1-Digit Number | Understand the Concept one Digit Number |Video
Mar 07, 25 03:55 PM
Understand the concept of adding 1-digit number with the help of objects as well as numbers. -
Vertical Addition | How to Add 1-Digit Number Vertically? | Problems
Mar 07, 25 02:35 PM
Now we will learn simple Vertical Addition of 1-digit number by arranging them one number under the other number. How to add 1-digit number vertically?



New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below. Ask a Question or Answer a Question.